
World Biomes, All You Want to Know About Its 2 Types
Our planet earth is vastly rich and hosts diverse forms of living organisms. A biome is any collection of a large group of ecosystems that have similar climates (temperature and amount of rainfall) and living organisms (plants and animals). Some people define them as “life zones” to make it easier for readers.
But what is an ecosystem, you might be wondering?
Well, an ecosystem is a specific area where living organisms live together as one unit and interact with each other. It comes in different sizes and conditions. An ecosystem could be as small as a lake or pond or as big as a desert. A well-established balance is pivotal to the survival of all living organisms within these ecosystems.
The main items that help keep the ecosystem in balance and alive include:
- Water
- Food
- Sun
- Oxygen, carbon, and nitrogen
Now back to the bigger picture, biomes.
You can find many different classifications of biomes on our planet, but for this time, we are going to stick to one simple classification.
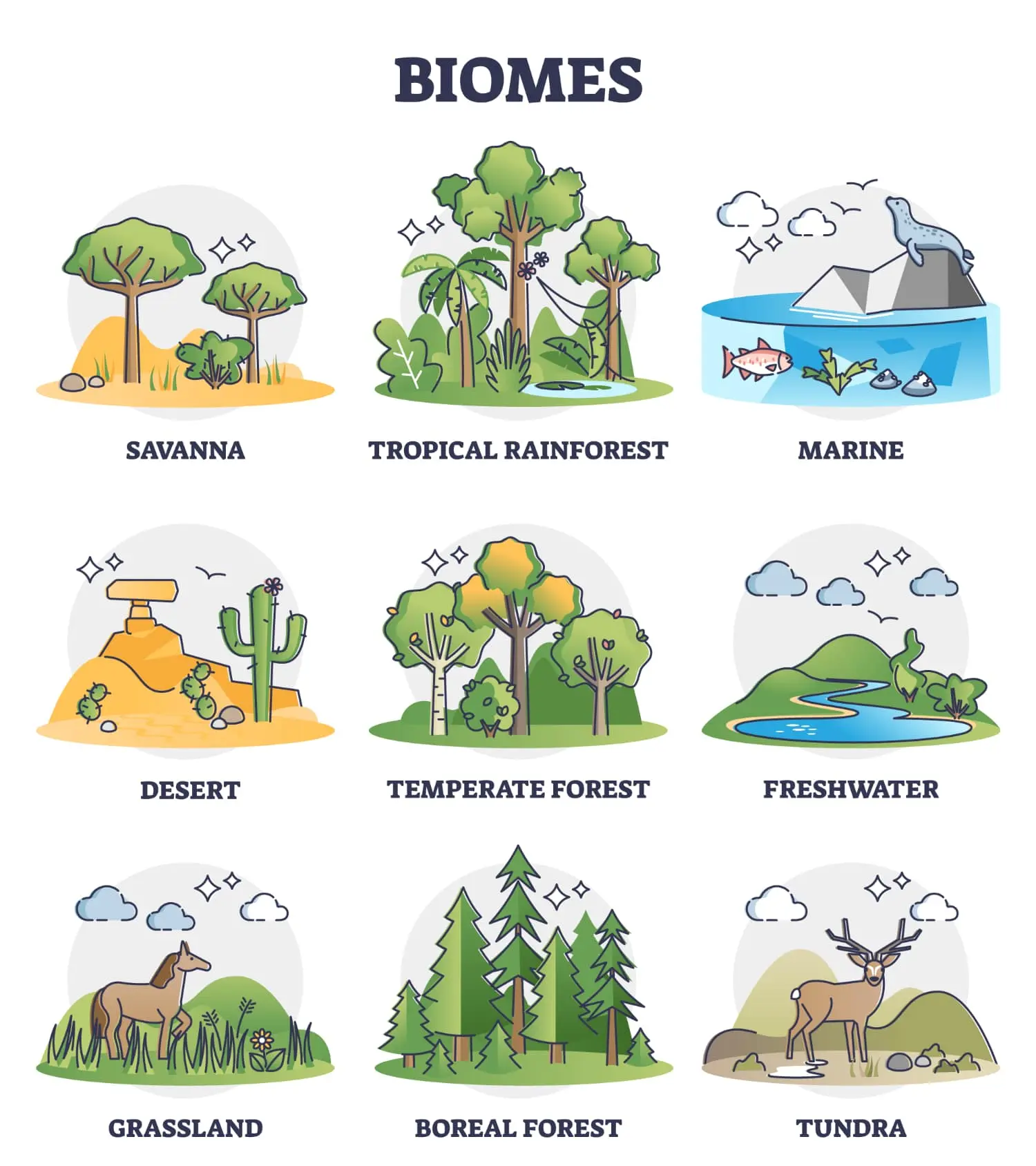
We can simply classify them into two main categories:
These are the widest and largest biomes on earth. That is because water covers more than 70% of our planet’s surface. They are found in major water bodies.
Water biomes are further classified into:
These biomes are present on Earth and make up less than 30% of our planet’s surface. They are further classified into:
In the following sections, we briefly examine each category separately.
Let’s start with water biomes.
1. Aquatic (Water) biomes
As mentioned above, they include freshwater and marine.
Freshwater biomes
The name freshwater comes from the low concentration of salt in this water. Freshwater biomes are pivotal for our lives, as they provide fish to eat and fresh water to drink. People have also used freshwater bodies like rivers to generate hydroelectric power through dams.
Freshwater biomes can be further subdivided into three main categories as follows:
- Lakes and ponds which have still water.
- Rivers and streams which have moving water.
- Wetlands which are a combination of land and water.
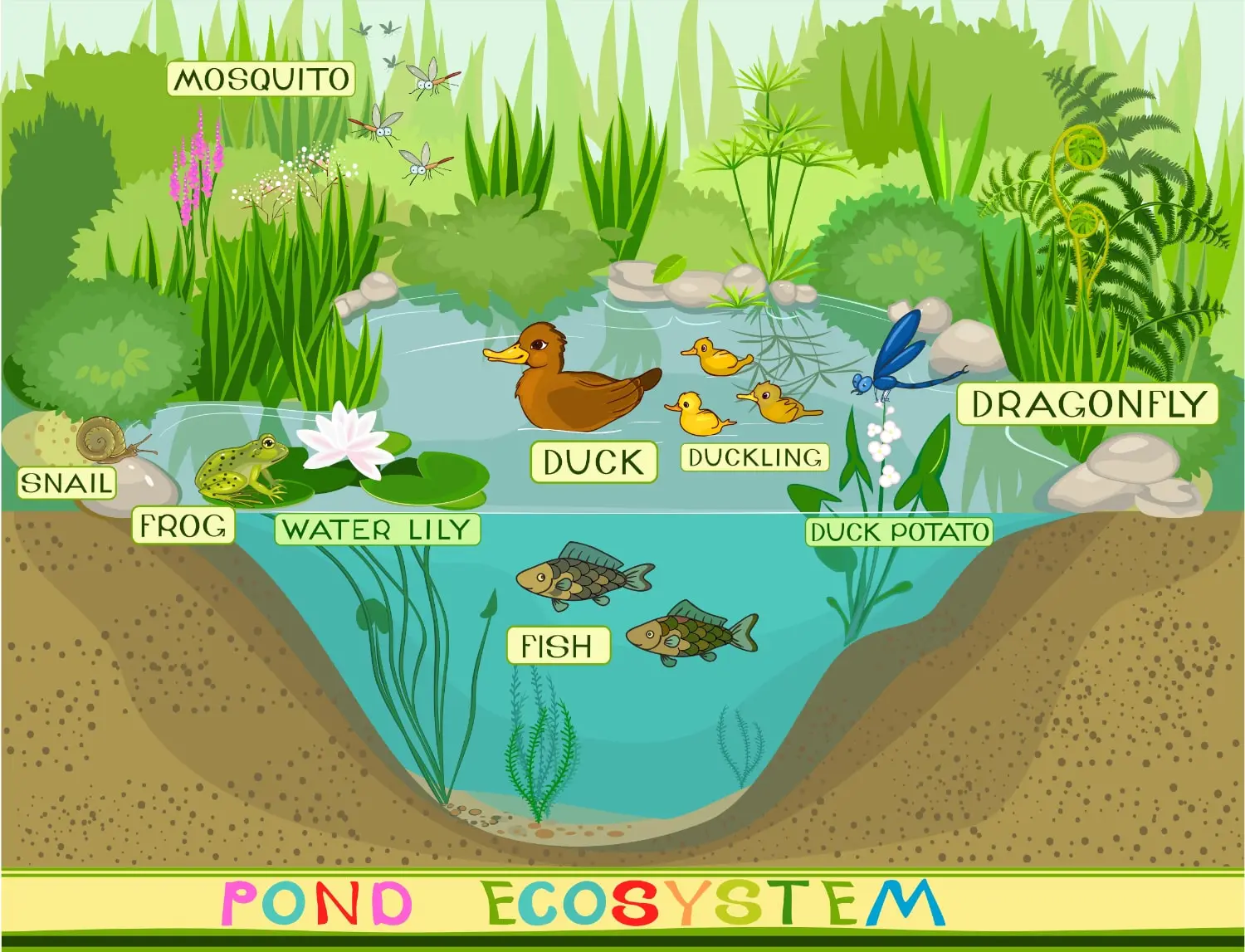
Lakes are large bodies of still freshwater surrounded by land.
Ponds are small bodies of still freshwater surrounded by land.
Rivers and streams are moving freshwater. They usually originate in mountains or from groundwater or even melting ice. They eventually end up in the oceans or seas. For example, the Amazon River in South America originates in the Andes Mountains and eventually flows into the Atlantic Ocean.
Wetlands (also known as swamp, marsh, bog, fen, mire, or slough). They are characterized by having water that covers their soil (areas with wet soil).
Dominant wildlife
Animals that can survive in freshwater include fish, amphibians (frogs, salamanders, and toads), snakes, alligators, otters, beavers, birds, insects (especially mosquitos), and turtles.
Dominant plants
Algae are commonly seen in still water (lakes and ponds). In moving water bodies (rivers and streams), plants have adapted to the fast-moving water by anchoring their roots or pending their stems easily with water movement. This adaptation protects plants in moving water bodies from being carried away by the water.
The most commonly seen plants in freshwater include algae, lilies, mosses, cattails, and duckweed plants.
Marine biomes
This is the largest biome on earth. It covers around 70% of the earth’s surface. Marine water has a high concentration of salt. It can be further subdivided into smaller biomes according to the temperature, nutrients, and amount of sunlight in the water. They play a major role in adjusting the weather on earth. Their water evaporates and gives us rain.
They also produce currents and waves that might be cold or warm and have a direct effect on the land that surrounds them. The temperature in oceans differs according to the depth of water. For example, in the superficial layers of water, the sun’s rays can easily penetrate the surface, and thus the water is warm. While deep down, where the sun’s rays can’t go, it is freezing cold and so dark.
Marine biomes include the five main oceans on our planet together with some smaller bays, gulfs, and coral reefs as follows:
- The Atlantic Ocean
- The Pacific Ocean
- The Indian Ocean
- The Arctic Ocean
- The Southern (Antarctic) Ocean
- Coral reefs. These are found in clear, tropical oceans. They are built up by tiny organisms called polyps
Dominant wildlife
Fish, sharks, octopuses, crustaceans, sea horses, dolphins, seals, and whales are all found in marine biomes.
The blue whale, the largest animal on our planet, lives in the ocean.
Dominant plants
Marine plants and algae are so important to us as they provide more than half of the oxygen in our planet’s atmosphere. They do so by a process called photosynthesis, through which they take in carbon dioxide from the air and give us oxygen that we can breathe. In fact, we can’t live without these algae.
Did you know that the area where freshwater gets mixed with seawater is called an estuary?
2. Terrestrial (land) biomes
There are different classifications of terrestrial biomes. We are going to discover them from the north, starting from the polar regions, and move down to the south.
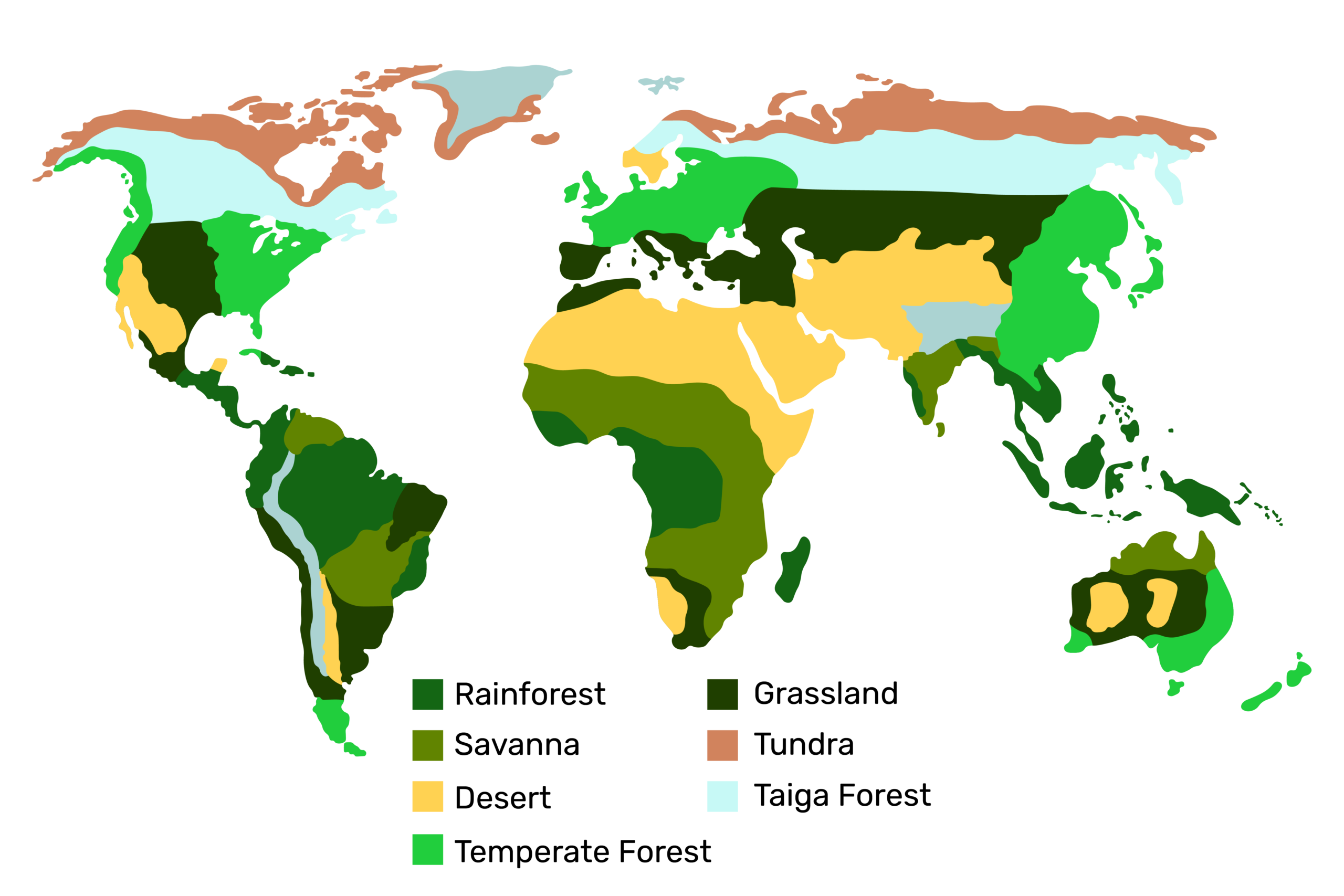
Tundra
Starting with the earth’s coldest and driest biome, Tundra. It lies close to the north and south poles. It has a permanently frozen subsoil layer that is called permafrost. Its harsh condition makes it hard for both animals and plants to survive.
That is why there is low biodiversity in this biome. Here you can only experience two seasons; a long dark winter and a very short summer. Rainfall is also so scanty here in the Tundra.
Dominant wildlife
In the Tundra, you can see polar bears, arctic foxes, arctic hares, musk oxen, lemmings, caribou, walruses, whales, and seals. Some birds visit Tundra in the summer and then migrate when it’s winter to warmer places.
Dominant plants
The main plants seen here are mosses, lichens, small shrubs, and short grasses. There are no trees in Tundra.
Taiga (Boreal/ Coniferous Forest)
Taiga is the largest of all the land biomes on Earth. It lies just south of the Tundra. It hosts more wildlife than the Tundra as the temperature here is less cold.
The boreal forest is sometimes called a coniferous forest as the predominant plant there is the coniferous trees. Here you can also experience two seasons; a long dark winter and a short, mild, wet summer.
Dominant wildlife
The cold weather of Taiga makes it difficult for animals to live there. However, some animals have adapted to this harsh weather by developing thick fur that insulates their bodies or by hibernating in the cold winters.
These animals include bears, wolves, lynxes, elks, deer, moose, hares, moles, squirrels, and migratory birds.
Dominant plants
Coniferous (evergreen) trees are the most common type of plants found in this land biome. They have needle-like leaves, and their seeds are produced in cones. Coniferous trees include pines, firs, and spruces.
Temperate Forest
Also known as a deciduous forest according to the most predominant type of trees there, the deciduous trees (leaf-shedding trees). In the temperate forest, you can experience the four seasons; winter, summer, spring, and autumn. They are considered the second rainiest biome after the tropical rainforests.
Dominant wildlife
Black bears, foxes, wolves, elks, coyotes, rabbits, deer, squirrels, and birds like woodpeckers are all animals found in temperate forests.
Dominant plants
The most commonly seen trees in the temperate forest are deciduous trees. These trees have leaves rather than the pine needles seen in Taiga. These deciduous trees lose their leaves each year in the winter and grow them back the next year in a cyclic manner.
Grassland
Grasslands, as their name implies, have a huge amount of grass. It is not common to see long trees there as the amount of rain is not enough to grow tall trees.
Grasslands have different names according to where they are. Sometimes, they are called prairies in North America. But in Europe and Asia, they are known as steppes.
In South America, people call them pampas. While in South Africa, they are veldts. Fires are very common in grasslands, whether occurring naturally from lightning or due to human activities.
Dominant wildlife
You can see massive herds of grazing animals travel the grassland together. These animals include bison, antelope, deer, and horses.
Dominant plants
As mentioned above, the grass is the dominant plant in grasslands. Trees and long shrubs are rarely seen there.
Desert
Deserts have a very low amount of rainfall, and that is why it’s so dry there. Some deserts are hot, and others are cold. The temperature in the desert fluctuates across the day, being so hot in the morning and freezing cold at night.
This extreme swing in temperature is due to the fact that deserts are dry. So when they get hot during the day, they can’t hold the heat from the sun and thus drop to colder temperatures at night.
The Sahara in Africa is the largest hot desert on Earth, while Antarctica is the largest cold desert in the world.
Dominant wildlife
The main animal people associate with the desert is the camel. Many types of reptiles are found in the desert, such as snakes, lizards, and tortoises. Birds like owls and hawks are also found there. You can also see other animals, including foxes and hares.
Dominant plants
Cactus plants are very common desert plants. You can also see grasses, shrubs and some small trees there too.
Savanna
Sometimes called tropical grassland. It covers half the surface of Africa and is also found in Australia, India, and South America. The climate there is usually warm all year round. Fires are also common here, as in grasslands.
Dominant wildlife
Large animals like elephants are seen in the Savannas. You can also see lots of different animals there, like; Zebras, giraffes, horses, and birds.
Dominant plants
Savannas have lots of grasses and a few scattered trees.
Tropical Rainforest
Situated close to the equator, Tropical rainforests, as their name implies, receive lots of rain around the year. It is considered the rainiest land biome. The weather here is humid and warm all year round. They are the most diverse land biomes on the planet. They have the greatest number of plant and animal species.
Dominant wildlife
Monkeys, sloths, jaguars, gorillas, birds such as parrots, and insects (like butterflies, mosquitoes, and ants) are some of the numerous species found in tropical rainforests.
Dominant plants
You can find countless species of plants in tropical rainforests. Scientists are still discovering new species. Orchids, vines, and bromeliads are commonly seen in tropical rainforests.
In the end, here’s a video explaining all these biomes we discussed above.
Conclusion
In the end, we want to draw your attention to a very serious and recent problem. That is, over the past decades, human activities have rapidly increased. As a consequence, these activities have drastically changed natural biomes on our planet by destroying and polluting them.
So it is becoming very urgent nowadays that we all pay extra attention to these biomes and how we can preserve them.
We don’t live alone on that planet, and we need to save plants and animals living with us from being destroyed or, even worse, becoming extinct.
Suppose we continue to do these harmful activities like polluting the water, overfishing, cutting down trees, burning fossil fuels, overhunting, and polluting the air.
In that case, we will definitely lose countless numbers of the most beautiful and diverse species of plants and animals, besides huge changes in the climate worldwide (which we have already started to see its consequences these days).
But you may ask, how could I help in solving this issue? I am still so young to change the policy of my own country.
Well, you can just spread the word to raise awareness on this urgent issue. As they say, every long journey starts with a single step. You can also join charitable organizations that support the environment in your country.
Here are ten simple steps to help in protecting our planet.
Before you go, here is a short quiz to test your understanding of the topic.
Q (1). Which of the following is the largest biome on Earth?
- Taiga(Boreal forest).
- Tropical rainforests.
- Marine biomes.
- Freshwater biomes.
Q (2). Which one of the following is the largest land biome on Earth?
- Tropical rainforests.
- Temperate forests.
- Grassland.
- Taiga (Boreal forest).
Q (3). A biome is defined as:
- A group of plants living together.
- A group of animals living together.
- A group of areas that have similar climatic conditions.
- A group of ecosystems that have similar climatic conditions and living organisms.
Q (4). Which one of the following statements is valid regarding biomes?
- Ecosystems are composed of large groups of biomes.
- Biomes are large groups of similar ecosystems.
- Land biomes make up more than 70% of the earth’s surface.
- Water biomes account for less than 30 % of the earth’s surface.
Q (5). Which of the following statement is false regarding water biomes?
- Water biomes cover more than 70% of the earth’s surface.
- Water biomes are further subdivided into freshwater and marine biomes.
- Marine biomes are the largest biome on our planet Earth.
- Freshwater biomes include the five major oceans and coral reefs.
Q (6). Which of the following sentences is true regarding land biomes?
- Land biomes cover less than 30% of the earth’s surface.
- Land biomes cover more than 70% of the earth’s surface.
- Taiga (boreal forest) is the smallest of all the land biomes.
- Tropical rainforests are characterized by having huge herds of grazing animals that travel together.
Q (7). The following statements about marine biomes are true except:
- Marine biomes provide us with most of the oxygen present in the atmosphere.
- Marine biomes cover up around 70% of the earth’s surface.
- Marine biomes include the five major oceans and coral reefs.
- Marine biomes include lakes, ponds, rivers, streams, and wetlands.
Q (8). The following sentence best describes the Savannas:
- It is the largest land biome on our planet.
- It is sometimes called tropical rainforest.
- It is full of grass and a few scattered trees.
- It is characterized by having huge herds of grazing animals that travel together.
Q (9). The following statement best describes Taiga (boreal forest):
- It is the largest land biome on earth.
- It is characterized by having huge herds of grazing animals that travel together.
- It is the rainiest land biome on our planet.
- It has the most diverse animal and plant species.
Q (10). The following statements are all correct except:
- Permafrost is a subsoil frozen layer seen in Tundra.
- Coniferous trees are most predominantly found in Taiga (boreal forest).
- Deciduous forest is another name for the temperate forest.
- The tropical rainforest is the coldest biome on earth.
The correct answers.
Q (1) – 3
Q (2) – 4
Q (3) – 4
Q (4) – 2
Q (5) – 4
Q (6) – 1
Q (7) – 4
Q (8) – 3
Q (9) – 1
Q (10) – 4
Some relevant articles that might interest you:
- Want to know more about how plants grow and their life cycle?
- To learn more about tectonic plates.
- Check out this one to know more about the biggest animals on Earth.
- Want to know more about the weather?
- Check out this article to know more about some remarkable seas and lakes on Earth.
- To learn more about the world’s 10 most amazing deserts.
- Check out this article to discover more about land animals from Africa and South America.
Why not subscribe to our LearningMole Library for as little as £1.99 per month to access over 1300 fun educational videos.


Leave a Reply