
8 Remarkable Seas and Lakes on Earth
Water Everywhere
Since the origin of the Solar System, it has been pretty clear that Earth is quite distinctive among all other seven planets. Earth is different not because it is blue as there are two other near-twins blue giants known as Uranus and Neptune but because of other interesting factors.
Neither is Earth unique because it is rocky as there are three other rocky planets in the inner Solar System. However, Earth is quite a different planet because it is the only planet that is known for having liquid water.
And liquid water is what makes life on Earth possible.
Table of Contents
There are many factors that influence the existence of liquid water on Earth. One of these factors is the Earth’s distance from the Sun. Since we are not too close to the Sun, water does not vaporize. And because we are not too far away as well, water does not freeze. Perfect distance, liquid water.
One might wonder, how did water originate on Earth? Well, that is a very legitimate question that agonized scientists for so many years. According to them, there are some theories that try to explain that.
Some theories claim that water was delivered to Earth by other objects that hit our planet billions of years ago. Others hypothesize that it was the hydrogen on Earth that allowed the formation of water.
Whatever the way in which water existed on Earth is, the result is the same. We have water. A lot of water.
With only less than one-third of the Earth’s surface being land, the remaining area, 71%, is covered in water. This huge area of water is classified into two main things: saltwater which occupies 97% of all the water on the planet and freshwater with a percentage of only 3%.
It is not just water that makes life on Earth possible. It is the freshwater that we need for drinking and growing crops.
Bodies of water
Water on Earth does not exist in one big body but rather in multiple bodies that differ in characteristics. Some bodies are connected to one another; others are independent. Some water bodies are exclusive to saltwater or freshwater while others can be both saltwater and freshwater.
In general, there are six main types of water bodies: oceans, seas, gulfs, bays, lakes, and rivers. That being said, there are other types that are classified based on different subfeatures. Some of these main classifications are fixed and others are interchangeably used, which can make it quite confusing as we will see later.
Oceans are vast bodies of saltwater that exist between continents. For example, the Pacific Ocean which is also the largest and deepest ocean on Earth separates Asia and The Americas.
Seas are smaller saltwater bodies than oceans. They are partially surrounded by land but still connected to other seas or oceans. Take for example the Red Sea. It is surrounded by land from almost all sides but connects to the Arabian Sea through the tiny Gulf of Aden.
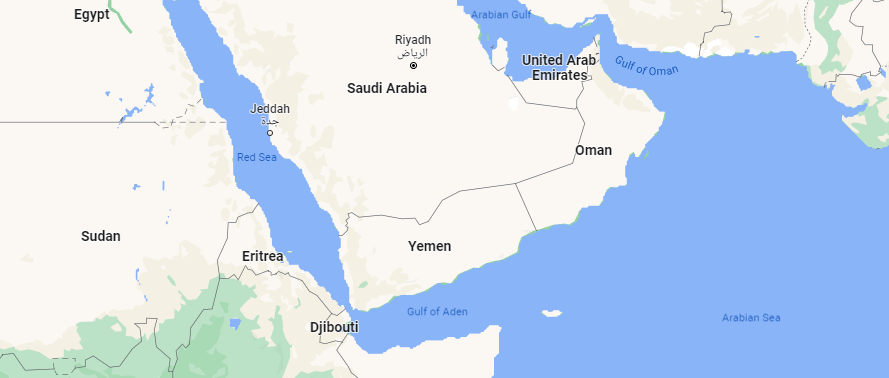
Gulfs and bays might seem the same but they are not, according to scientists. Both are surrounded by land from three sides. The fourth side, however, is connected to a water body; sea, ocean, or even rivers and lakes.
Telling the difference between gulfs and bays is pretty challenging. Some say the difference is the size. They claim that gulfs are much larger than bays. This is true when comparing the Gulf of Mexico to the San Francisco Bay, for instance.
However, such a definition does not work for the Bay of Bengal in the Indian Ocean and the Gulf of Suez in Egypt. The Bay of Bengal is very large compared to the small Gulf of Suez.
Others say that the only difference between gulfs and bays is defined based on the size of the opening which connects them to other water bodies. If the opening is very wide, it is called a bay. If the opening is narrow, it is a gulf.
Similarly, this definition does not apply to the example we have mentioned earlier. We can clearly see that the opening of the San Francisco Bay is quite narrow; however, that of the Gulf of Mexico is pretty wide.
We can just conclude that there does not seem to be quite a definite rule to distinguish between gulf and bays.
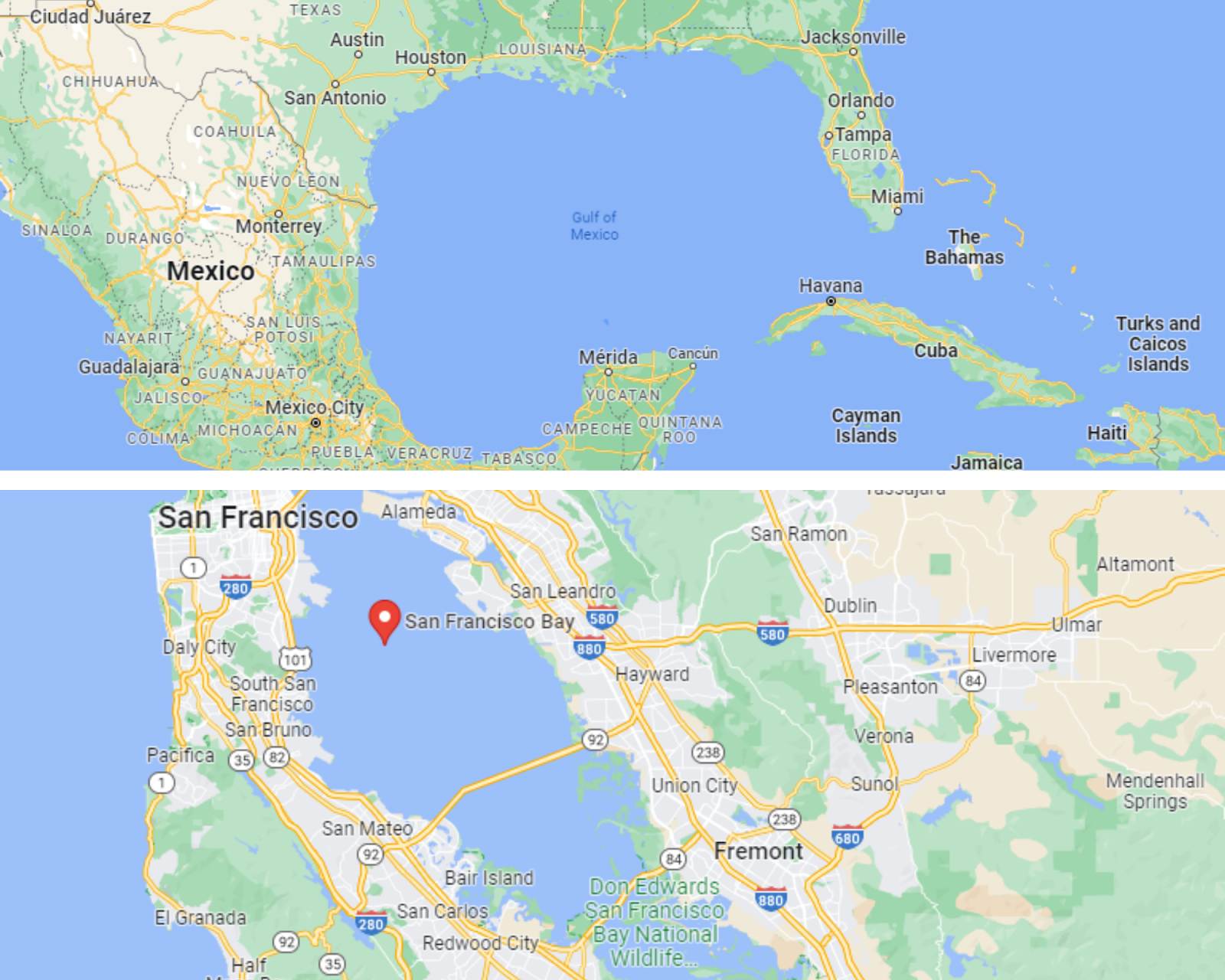
Then we have lakes. Lakes are surrounded by land from all sides. They are completely independent of seas and oceans. Lakes can be of freshwater such as Lake Victoria in Africa. They can be of saltwater too like the Great Salt Lake in Utah, USA.
That being said, sometimes, for some reason, lakes are referred to as seas though they are a lot smaller than seas. For example, the Caspian Sea in Iran is in fact the largest lake in the world. Still, it is called a sea even though it is completely surrounded by land and disconnected from other oceans. Similarly, the Dead Sea in Jordan is originally a lake.
It is worth mentioning here that the water in all the bodies mentioned above is still. Although it rises and falls due to the wind, it does not go anywhere else. It does not flow. When water flows from one end to another, the water body is hence called a river, a stream, and sometimes a canal.
Rivers are large naturally-formed streams of water that flow from one end downhill to another. All rivers usually flow into other water bodies such as seas, lakes, or even other rivers.
All the water bodies we previously discussed are mostly characterized by size. Yet, rivers are rather characterized by lengths. The longest river in the world is the River Nile which flows through Africa followed by the Amazon River in South America.
Now, let’s look exclusively into two distinct water bodies.
Seas
The term sea is used by scientists to describe large bodies of saltwater we know as oceans. However, the same term is also used to describe smaller bodies of saltwater which scientists call marginal seas to differentiate them from the ocean.
Seas are called marginal due to their main characteristic of being on the margins of oceans. Seas are enclosed by lands from almost all sides but they are connected to oceans as well through straits. Seas are also less deep than oceans.
Seas play a vital role in influencing the weather of Earth. In fact, they help keep our planet warm by distributing the heat all over the globe. Here is how it happens.
The heat from the Sun causes the seawater to evaporate and turn from liquid water to water vapor. Water vapor increases the humidity level in the air and forms clouds. Clouds are delivered to every other place on the planet by the wind and cause rain.
Another reason that makes seas important is that they provide us with a medium through which we can move by ships from one land to another far one. This influences trade and facilitates moving goods between countries.
Additionally, seas are abundant with deliciously edible fish. Seashores are good places for recreation, leisure, and enjoying great vacations.
Waves
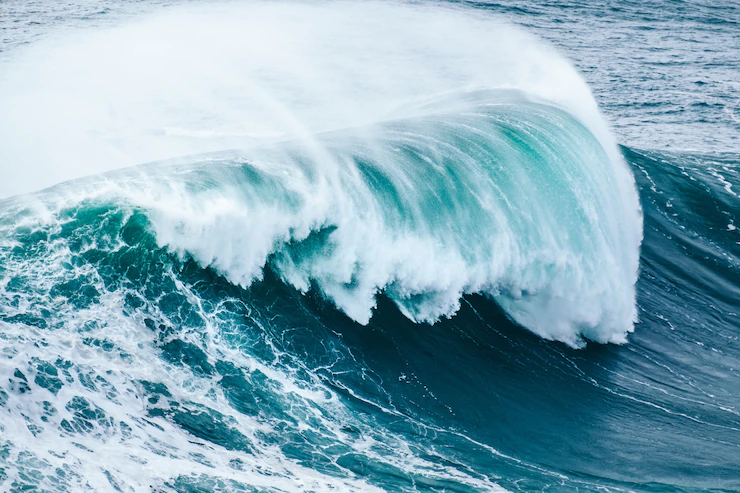

One thing that characterizes seas is waves. When the wind blows, it hits the surface of the water and causes water to rise to form waves. The stronger the wind blows, the larger and higher the waves are.
Waves then travel in the sea as the wind pushes them. When the waves travel at the same speed as the wind, they reach their maximum height. Interestingly, the highest wave ever recorded was 19 m. It was measured in February 2013.
Waves keep traveling from open water until they enter the shallow water. This is when they slow down and grow in height. They keep moving until they break, creating foam, and reach land.
We are all familiar with waves. They are all fun and entertaining. Wave sports such as surfing are also very popular. Everything is good as long as waves are nice and tame. However, when they go crazy, they turn into grave danger to everything on land.
Tsunamis
Scientists call wild crazy waves tsunamis. Tsunamis do not form by wind moving the water surface. Rather, they are formed by extreme events such as underwater earthquakes, meteorite impacts— very large objects hitting the sea from outer space—or volcanic eruptions. Such events raise or lower the sea floor causing water to form waves that move very fast.
While normal wind-generated waves break as they reach land, tsunamis do not. They keep traveling at high speeds until they reach land, flooding everything they find in their way. As a tsunami wave drains back to the sea, it drags things and people with it causing huge destruction.
One of the most destructive tsunamis is that which happened in 2004. It was mainly caused by an earthquake in the Indian Ocean. Such a tsunami caused great destruction in the coastal areas of many countries such as Indonesia, Sri Lanka, and Thailand.
Tides
Among the changes that seawater experiences are tides. Tides are defined as the increase and decrease of water level influenced mostly by the Moon’s gravity as well as that of the Sun and the rotation of Earth.
Because the Moon is much closer to Earth than the Sun, it exerts a stronger gravitational pull on Earth. This pull creates what scientists call the tidal force. During the time Earth is the closest to the Moon, the tidal force causes the water to bulge out. This means the water level increases. Think of it as if the Moon is pulling the water out. This is called a high tide.
The opposite is also true. When Earth is the farthest from the Moon, the Moon’s gravity is the weakest. So the water level decreases. This is called a low tide. Low tides are characterized by shorelines with water pulled back.
Tides are quite important to Earth for several reasons. Due to the water movement, tides help move the warm water from places near the Equator to the poles where the water is very cold. This mixing of water balances the temperature on the planet and creates more habitable weather conditions.
Some of the luckiest people during times of tides are fishermen. That is because they can catch large numbers of fish in less time because many edible fish species are known to concentrate in areas where the tide is low.
Tides are also used to help clean the environment by generating renewable energy. The rise and fall of water level caused by tides are used to move turbines that generate electricity.
Water cycle
Though they are saltwater, seas help freshwater to reach us as well as plants and animals. This is known as the water cycle.
The water cycle is defined as the continuous movement of water. Seas absorb sunlight and heat from the Sun. The heat causes water to vaporize, leaving behind salts. Water vapor forms clouds. Clouds move to different places pushed by the wind. When clouds get too heavy, they drop water back to Earth in the form of rain and snow.
3 Examples of Incredible Seas
There is a tremendous number of seas on Earth. They differ in areas, weather, characteristics, and even the number of countries they are surrounded by. In this section, we are going to explore some of the most important seas in the world.
Arabian Sea
One of the most important seas in the world is the Arabian Sea which is found in the northern Indian Ocean. The Arabian sea is surrounded by Pakistan, Iran, and the Gulf of Oman to the north, the Gulf of Aden on the Arabian Peninsula to the west, the Laccadive Sea and the Maldives to the southeast, Somalia to the southwest, and India to the east.
Through the Strait of Bab-el-Mandeb, the Arabian Sea is connected to the Gulf of Aden and the Red Sea while the Gulf of Oman connects it to the Persian Gulf.
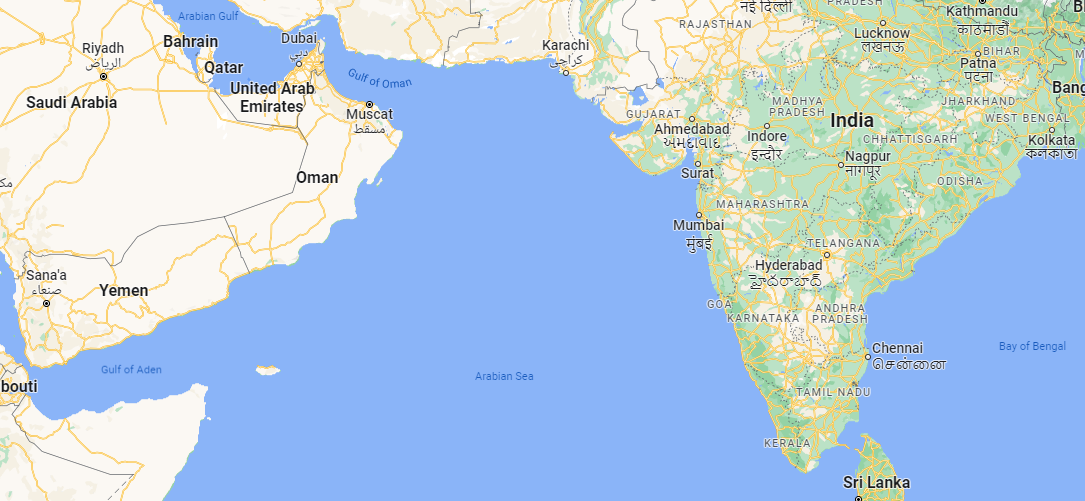
The Arabian Sea is quite large. It comprises an area of 3.86 million km2. The deepest point is 4,652 m underwater. There are multiple rivers that flow into the Arabian Sea as well.
The importance of seas or any water bodies can be determined based on whether or not they are a trade route. Trade routes are water bodies through which ships carrying goods travel from one country to another, very far one. In this, the Arabian Sea is super vital.
Since prehistoric times, the Arabian Sea has been used as a major trade route providing a link between India in the east to Europe in the north. Ships carrying different goods sail across the Arabian Sea, enter the Red Sea through the Strait of Bab-el-Mandeb, and move up and reach the Mediterranean Sea by sailing through the Suez Canal.
Once in the Mediterranean Sea, ships can easily reach any country bordering the Mediterranean.
Mediterranean Sea
Like the Arabian Sea, one of the most important seas in the entire world is the Mediterranean Sea. It comes in sixth place among the largest seas in the world with a total area of 2.5 million km2.
The Mediterranean Sea is almost completely enclosed by land. A total of 20 countries surround the sea, most of which are found in southern Europe and North Africa.
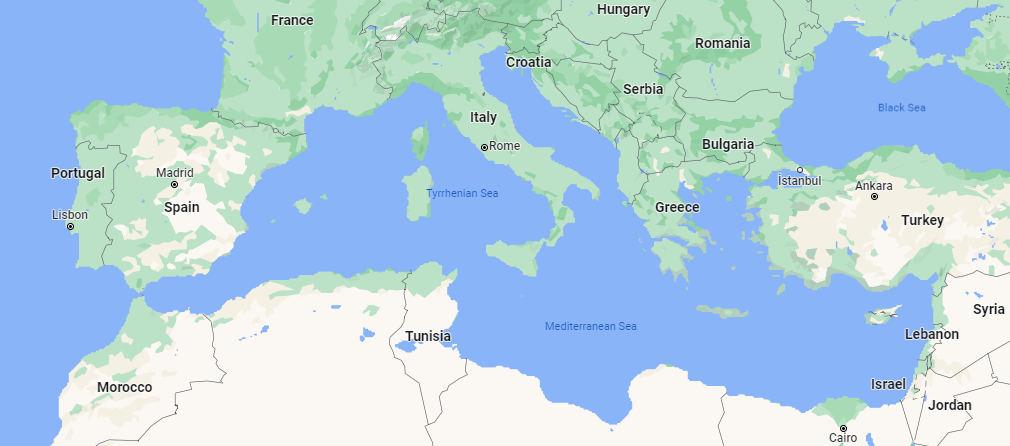
Some of these countries that share a coast with the Mediterranean Sea are Egypt, Algeria, Tunisia, and Morocco in Africa and Italy, France, Spain, and Croatia in Europe.
There is a large number of islands in the Mediterranean Sea as well. Actually, there are more than 3300 islands, the largest of them being Sicily whose total area is 27,711 m2.
On the other hand, the smallest island is Tabarca. It is 1,800 meters long and 500 meters wide. That means an adult can cross the island in less than five minutes and go from side to side in only 15 minutes or so.
It is good to mention here that Sicily is part of Italy while Tabarca is Spanish.
The Mediterranean Sea is connected to the Atlantic Ocean through the tiny Strait of Gibraltar. You can think of it as a corridor through which ships pass from the sea to the open water of the Atlantic Ocean.
The Strait of Gibraltar is 13 km wide and separates Spain and Portugal in Europe from Morocco in Africa.
One reason that makes the Mediterranean Sea quite important is that it provides a shorter way for ships coming from Eastern Asia and heading toward Europe. This is because the Mediterranean Sea is connected to the Red Sea by the Suez Canal in Egypt.
So instead of ships traveling from India, for example, going all the way around Africa to reach Europe, they would rather enter the Red Sea, pass through the Suez Canal, enter the Mediterranean Sea, and sail across it to reach Europe. This saves so much time and money as well.
Both the River Nile passing through Africa and the Ebro in Spain flow into the Mediterranean Sea.
Adriatic Sea
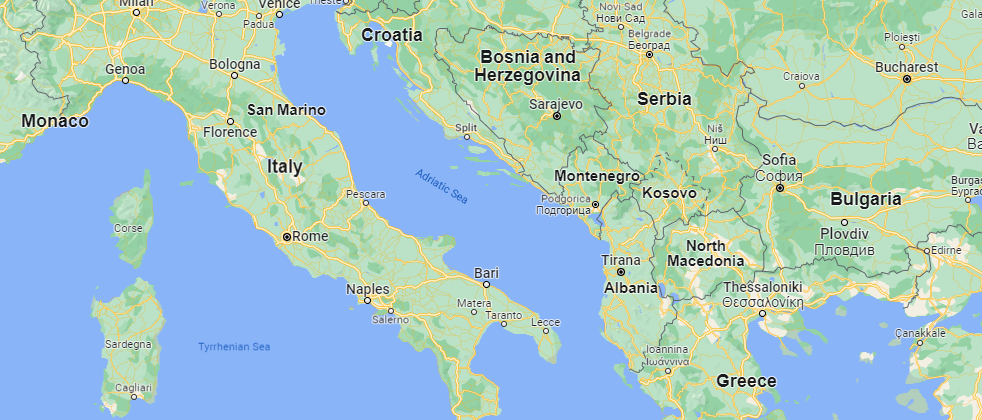
Connected from the north to the Mediterranean Sea is the Adriatic Sea. It is the smallest sea in the world with an area of only 138,600 km2. It separates Italy from the southeastern European countries including Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, and Albania.
Despite its relatively small area, the Adriatic Sea has more than 1300 islands, most of which are along the Croatian coast. While the sea is the shallowest in the north, its deepest point is found in the south at 1,233 m underwater.
Since the River Nile flows into the Mediterranean Sea, one-third of this freshwater is collected in the Adriatic Sea. That is why it is less salty than the Mediterranean Sea itself.
The Adriatic Sea and its coasts are a perfect vacation destination thanks to its very moderate weather. While surface water temperature is usually 12 °C in winter, it rises to 30 °C in summer.
Venice, the famous water city of Italy, is bordered by the Adriatic Sea as well as multiple other cities, making them amazing vacation spots for millions of tourists.
Lakes
A lake is a body of slow-moving or still water that is surrounded by land from all sides. Unlike seas, lakes are not connected nor are they a part of oceans. Most lakes are connected only to rivers and streams. These are long narrow channels through which freshwater flows. Rivers can either flow into or out of lakes.
The water in lakes usually comes from rain, snow, melting ice, or from underground. Though most lakes are freshwater, there are many saltwater lakes as well. The majority of lakes are freshwater. That means they existed during the formation of Earth millions of years ago and according to the changes that our planet experienced throughout its history.
Besides natural lakes, there are artificial lakes as well. There are lakes that humans build mainly to store water, irrigate plants, and generate electricity. The largest man-made lake by area is Lake Volta in Ghana. It is 8,502 km2.
On Earth, there are 117 million lakes of different characteristics related to size, area, salinity, and even watercolor. At least two million of these lakes are found in Canada only.
Some lakes are very small; they do not even appear on maps nor can be caught by satellites. Other lakes are so big that they are referred to as seas. An example of this is the Caspian Sea in Asia which is 371,000 km2 in area.
Compared to oceans and seas, lakes are way shallower. The deepest lake on Earth is Lake Baikal in Siberia, Russia. It has a maximum depth of just 1.6 km.
Another way to classify lakes is by determining whether they are open or closed. When water leaves the lake into a river, it is called an open lake. However, if no water leaves the lake to any river or stream but only by evaporation, it is called a closed lake.
All freshwater lakes are open because they are all connected to rivers and other streams. That means closed lakes are saltwater. This is because when water evaporates and turns into water vapor, it leaves behind salt. So the remaining water becomes salty.
Lakes are important not only because they store water and provide a good source for drinking and watering plants. They also attract tourists. Many lakes are beautiful tourist destinations where people can enjoy swimming, sailing, water skiing, and fishing. The areas around lakes are perfect spots for picnics and camping too.
Lakes also provide a good route for traveling and moving from one place to another through the streams that are connected to them.
Here we come to explore some of the most distinctive lakes in the world.
Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is in fact a very large lake but because it is very large, it is called a sea. It is 371,000 km2 in area which makes it the largest lake in the world.
The Caspian Sea lies between Asia and Europe with coasts shared with Iran, Turkmenistan, Russia, Azerbaijan, and Kazakhstan. The Volga River, which is the longest river in Europe, flows into the Caspian Sea from the north. Additionally, more than 130 other rivers flow into the Caspian Sea.
The maximum depth of the Caspian Sea is 1,025 m.
Around 34 islands are found in the Caspian Sea, most of which are near the coasts with the largest of them being Ogurja Ada.
Due to its oil industry, the Caspian Sea is very important. It is famous for being rich in oil and natural gas. That is why it is a global source of energy production. That being said, the result of this great oil industry is water pollution that harmed its marine life. The oil disposed of in the sea has bad effects and even kills fish and sea creatures.
The Caspian Sea is considered a closed lake. Despite the large number of rivers that flow into the sea, the seawater itself does not leave it except by evaporation. That is why it is a closed body of water.
Dead Sea
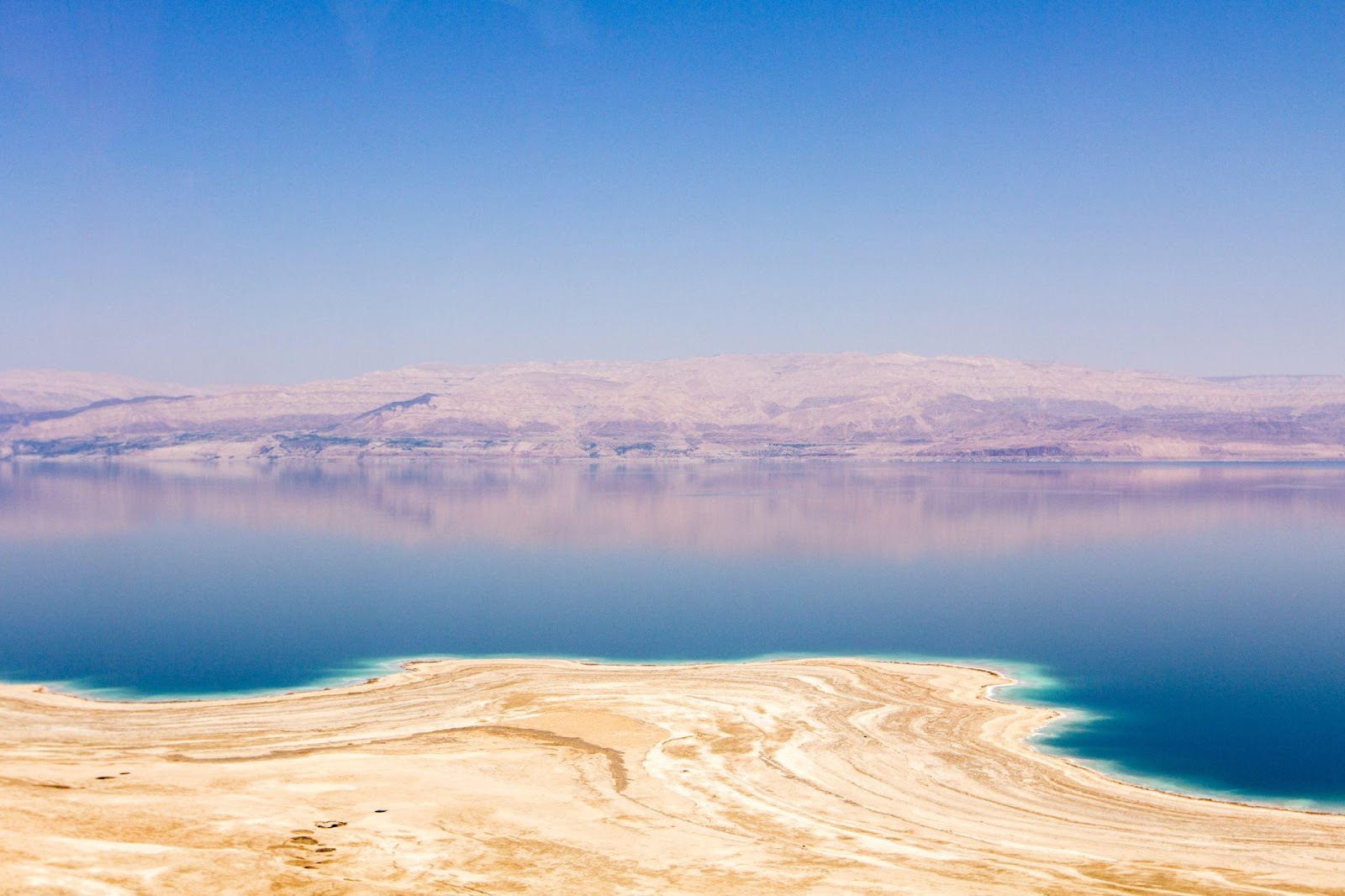

The Dead Sea is quite distinctive for multiple reasons: water salinity, name, and elevation.
Surrounded by mountains, the Dead Sea is in fact a small lake of 605 km2 in area that is enclosed by land from all sides. However, it is not really known why it is called a sea. Found in the Middle East, the Dead Sea is bordered by Jordan, Palestine, and Israel. The Jordan River flows into the Dead Sea.
One distinctive characteristic of the Dead Sea is its salinity. It is around 9.7 times saltier than the ocean. This makes it the saltiest water body on Earth. Such a high concentration of salt in the water increases buoyancy that no one can actually drown in it. Furthermore, one can easily stay on the surface without having to tread water to stay floating.
On the other hand, this too much salt makes it impossible for any plants or fish to survive in the Dead Sea. And this is how it got its name. Dead, because anything in it would be dead.
Another thing that makes the Dead Sea unique is its elevation. Or should we say minus elevation? The Dead Sea’s surface is already 430.5 m below sea level making it the lowest point on Earth. The Dead Sea is 306 m deep.
Despite its extreme salinity, the Dead Sea seems to have some benefits. Its mud is rich in minerals such as silicon, calcium, magnesium, iron sodium, potassium oxide, and phosphorus that are proven to reduce skin impurities, help cure arthritis and acne, and release back pain.
Unlike many other water bodies that seem to retain the same area they cover with water by the water cycle, the Dead Sea is shrinking. In 1930, the surface area of the Dead Sea was 1050 km2; however, it is now 605 km2. Some scientists believe that the Dead Sea will be completely gone by 2050.
The shrinking of the Dead Sea is happening for several reasons. First is the lack of water that feeds the sea. Despite the fact that the Jordan River is flowing into the Dead Sea, much of this freshwater is used for drinking and growing plants. That is why the Dead Sea is receiving less and less water.
Rains and floods are also a source of water for lakes. However, there has been a great lack of rain in the area around the Dead Sea. This is another reason why the sea is drying up.
The third reason that is influencing the slow death of the Dead Sea is being a closed lake. Water leaves the Dead Sea by evaporation which happens to be very strong there. This makes the lake lose its water at a faster rate.
To save the Dead Sea from disappearing, many ideas were proposed to connect the sea to either the Mediterranean Sea or the Red Sea to provide a new water source to feed it. However, these proposals were not accepted because building such canals will be very expensive.
Lake Victoria
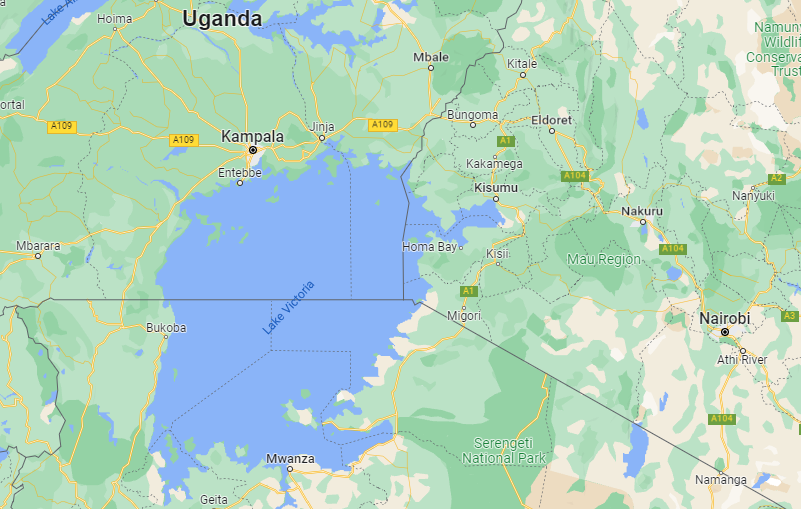
Lake Victoria in central Africa is the largest lake by area. It has a surface area of about 60,000 km2. It is also the world’s second-largest freshwater lake after Lake Superiority between the USA and Canada. The maximum depth of Lake Victoria is 84 m, which makes it quite shallow compared to other famous lakes.
Lake Victoria is believed to have formed 400,000 years ago. It receives 80% of its water from rain and the rest comes from the many rivers and thousands of streams that flow into it. Only the River Nile, the longest river in the world, flows out of Lake Victoria. Lake Victoria is the primary source of its water.
Tropical lakes are the lakes usually found around the Equator. Lake Victoria is the largest of them all. Being shared between three countries, around 49% of Lake Victoria is in Tanzania, 45% in Uganda and only 6% of it is found in Kenya.
Though all those countries have been familiar with the lake ever since it existed, the lake was pretty unknown to the rest of the world. It was not until British explorer John Hanning Speke started searching for the source of the River Nile that he finally reached Lake Victoria in 1858. The lake was named after Queen Victoria who was the queen of England at the time.
Lake Victoria is quite important for the countries within which it lies. Since it is abundant with fish, more than 200,000 people work in the fishing industry of Lake Victoria which provides food and major life necessities for them and millions of other people.
Unlike the Dead Sea which lies 430 m below sea level, Lake Victoria is 1,134 m above sea level. Interestingly, this huge lake completely dried out about 17,000 years ago but it filled again several thousand years after that.
Since its main water source is rain, Lake Victoria experiences heavy rainfall most of the year leaving only a short period of semi-dry weather.
With a spectacular coastline along which are many hotels and resorts, tourists flock to the lake usually in the months of June to August when the weather is cooler to enjoy a relaxing vacation and the beautiful scenery of the lake.
Laguna Colorada
We have mentioned earlier that there are multiple characteristics that set lakes apart. Among such characteristics are surface area, water volume, depth, salinity level, and the number of rivers or streams flowing into or out of the lake. However, another feature that can distinguish lakes is the color of the water.
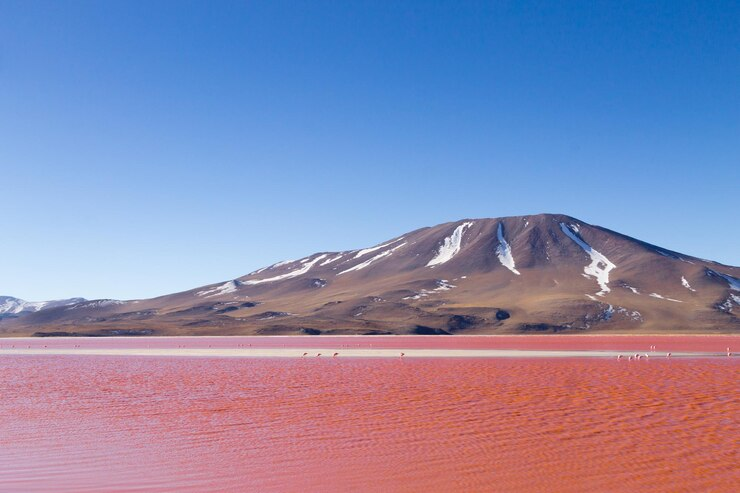
Though one might think that lakes’ waters usually look blue or green, some have red water. Laguna Colorada is one of these lakes. Located in Bolivia, South America, Laguna Colorada is named after its main red water feature. Laguna Colorada in Spanish literally means red lagoon in English.
The lake is 60 km2 in area. Though being relatively large, Laguna Colorada is very shallow. It has an average depth of only 35 cm and a maximum depth of 1.5 m! The lake primarily gets its water from Rio Sulor (River Sulor) that flows into it.
While the old local culture thought the red water of Laguna Colorada was the blood of the gods, this red color is actually caused by the different types of red algae that grow in the lake’s salty water as well as the red sediments settling on its floor.
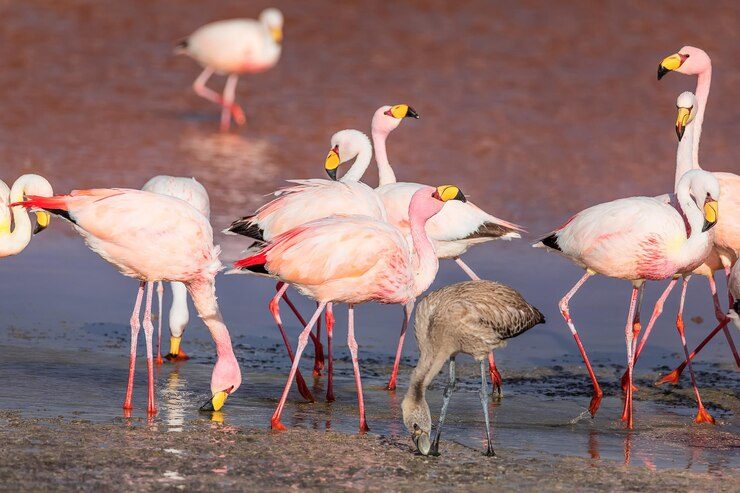
Another interesting feature that makes Laguna Colorada an incredibly beautiful destination for many tourists is flamingos. Among the six species of flamingos found in the entire world, three of them settle in the area of Laguna Colorada. Flocks of flamingos gather in the lake to eat plankton, the flamingos’ food the lake is rich in.
Flamingos also feed on the red algae, brine fly larvae, and brine shrimp found in large amounts in the lake. This food is full of the red pigment beta-carotene which when digested by the flamingos, turns their feathers pink. So pink flamingos live in the red lake. Makes sense.
Laguna Verde
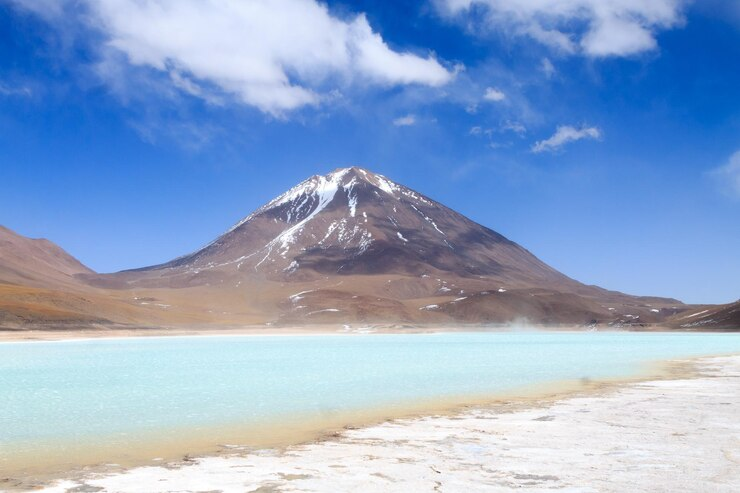

It seems like Bolivia has something for calling lakes after colors.
In contrast to Laguna Colorada we just discussed is the Laguna Verde or the green lake located also in Bolivia. Laguna Verde is a lot smaller and a bit deeper than Laguna Colorada. It has a surface area of 7.5 km2 and a depth of 5.4 m. Laguna Verde is located at the foot of a volcano called Licancabur.
The spectacular green color of Laguna Verde is attributed to the minerals that come out of the lake’s soil into the water. These minerals include arsenic, magnesium, carbonate, and calcium.
Because the lake is very beautiful, it is one of Bolivia’s most important tourist attractions.
Conclusion
Everything on planet Earth, including us, is made of water.
Though water may sound very simple: a colorless, tasteless, odorless liquid required for humans as well as all other creatures to survive, or maybe a chemical made of two hydrogen atoms combined by one oxygen atom, water is much much more than that.
Covering over 70% of the Earth’s surface, water is classified into different bodies that are different in many ways. Some bodies are saltwater only such as oceans, seas, and lakes. Others are freshwater only like rivers, streams, and lakes too.
In this article, we explored together the characteristics of two of the most important water bodies; seas and lakes. We learned that the term sea can be used to describe oceans; however, the term marginal sea would probably mean the seas we are familiar with.
We learned that seas cause different phenomena such as waves, tides, and other extreme events like tsunamis which are mainly caused by earthquakes and are quite destructive as well.
We then explored three of the world’s most notable seas: the Arabian Sea which is connected to the Indian Ocean, the Mediterranean Sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, and the Adriatic Sea which is the smallest sea in the world.
After that, we discussed lakes, what they are, where they get their water from, and the difference between closed and open lakes. Lakes can be very large and tiny as well. They can be of both freshwater and saltwater; however; the majority of lakes on Earth are freshwater.
Then we discussed some of the most interesting lakes. On top of those lakes were the Caspian Sea in Asia and the Dead Sea in Jordan which are lakes but no one knows why everyone calls them seas.
The Dead Sea is pretty interesting because it is the lowest point on Earth and the saltiest water body ever found on the planet. We also learned how it is shrinking and what plans can help save it from dying.
Next, we explored two of the world’s most distinctive lakes which are both located in Bolivia in South America: Laguna Colorada and Laguna Verde, or the red lake and green lake. These two lakes get their unique colors from the algae and minerals residing on their floor and coming out of the soil.
Lastly, we explained how such red algae in Laguna Colorada give flamingos their distinct pink color and how these two lakes are flocked yearly by thousands of tourists to enjoy their beautiful scenery.




Leave a Reply