
Gold: Your Guide to the Precious element
This guide aims to provide a description of the importance of the precious metal “Gold”, in man’s economic and artistic development throughout his history. We will discover together the origins of gold, its diffusion and its uses, going from ancient times to the present day. We will see how even today, gold represents a precious element able to fascinate and amaze from an artistic and emotional point of view, as well as being a valid and reliable form of investment.
History of Gold
Gold has been known and highly appreciated by men since prehistoric times. It was very probably the first metal ever used by the human species (before copper) for the manufacture of ornaments, jewels and ritual objects.

Gold in Ancient Egypt
Gold is mentioned in Egyptian texts (hieroglyphic), starting with the pharaoh Den, the first Egyptian dynasty, around 3,000 BC.
Indeed, Egypt and Nubia had enough resources to place them among the most important gold producers of the civilizations of ancient history. Especially in the period of formation of the Egyptian state, gold played both a political and an economic role: it was one of the elements at the origin of the deification of the pharaoh and the birth of cities.
There were many gold mines, and the Egyptians possessed the technology to extract and work on it,so that Nubia became an important production area gold-bearing for much of subsequent history.
The oldest known map of a gold mine was created during the 19th Dynasty of Ancient Egypt (1320-1200 BC), while the first written reference to gold was recorded in the Twelfth Dynasty, about 1900 BC.
The papyrus map preserved in the Egyptian Museum of Turin shows the plan of a gold mine in Nubia, together with indications on the geology of the place.
The discovery of America and the Gold rush
The history of gold assumes a very important role with European exploration of the Americas (starting from 1492) was encouraged by the reports of the first explorers, who narrated the large quantity of gold jewellery worn by the native populations, especially in Central America, Peru and Colombia.
In the 19th century, as many gold rushes erupted as there, goldfields were discovered, in particular: California, Colorado, Central Otago, Australia, the Witwatersrand, the Black Hills and the Klondike.
While geologically speaking, ancient gold was relatively easy to obtain, 75% of the gold produced has been mined since 1910. It is estimated that if all the refined gold in the world were melted down into a cube, the cube would have an edge of 20 meters (66 ft).
Thanks to its value and its resistance to corrosion, much of the gold mined throughout history is still in circulation today in some form.

The Alchemists and the search for Gold
Among the most intriguing historical notes on gold is that linked to alchemy. The proximity of atomic numbers made 20th-century scientists think of obtaining gold by bombarding mercury (in test tubes) with neutrons to get the transmutation of chemical elements.
The main aim of the alchemists was to produce gold from other substances, such as iron or lead. The alchemical symbol of gold was a circle with a dot in the centre, which is also the astrological symbol, the hieroglyphic symbol and the Chinese pictograph of the Sun. As for the modern attempts to obtain gold artificially.
Gold coins and the gold standard
Gold has long been regarded as one of the most valuable metals, and its value has served as the foundation for many countries’ currencies (known as the Gold Standard) in various historical periods.
The first gold coins were minted by King Croesus, ruler of Lydia, in western Asia Minor, from 560 BC. to 546 BC; in particular, the gold of Lydia came from the mines and from the sand of the river Pactolus.
Characteristics of Gold
Each element in nature has different characteristics that make it distinct from any other element.
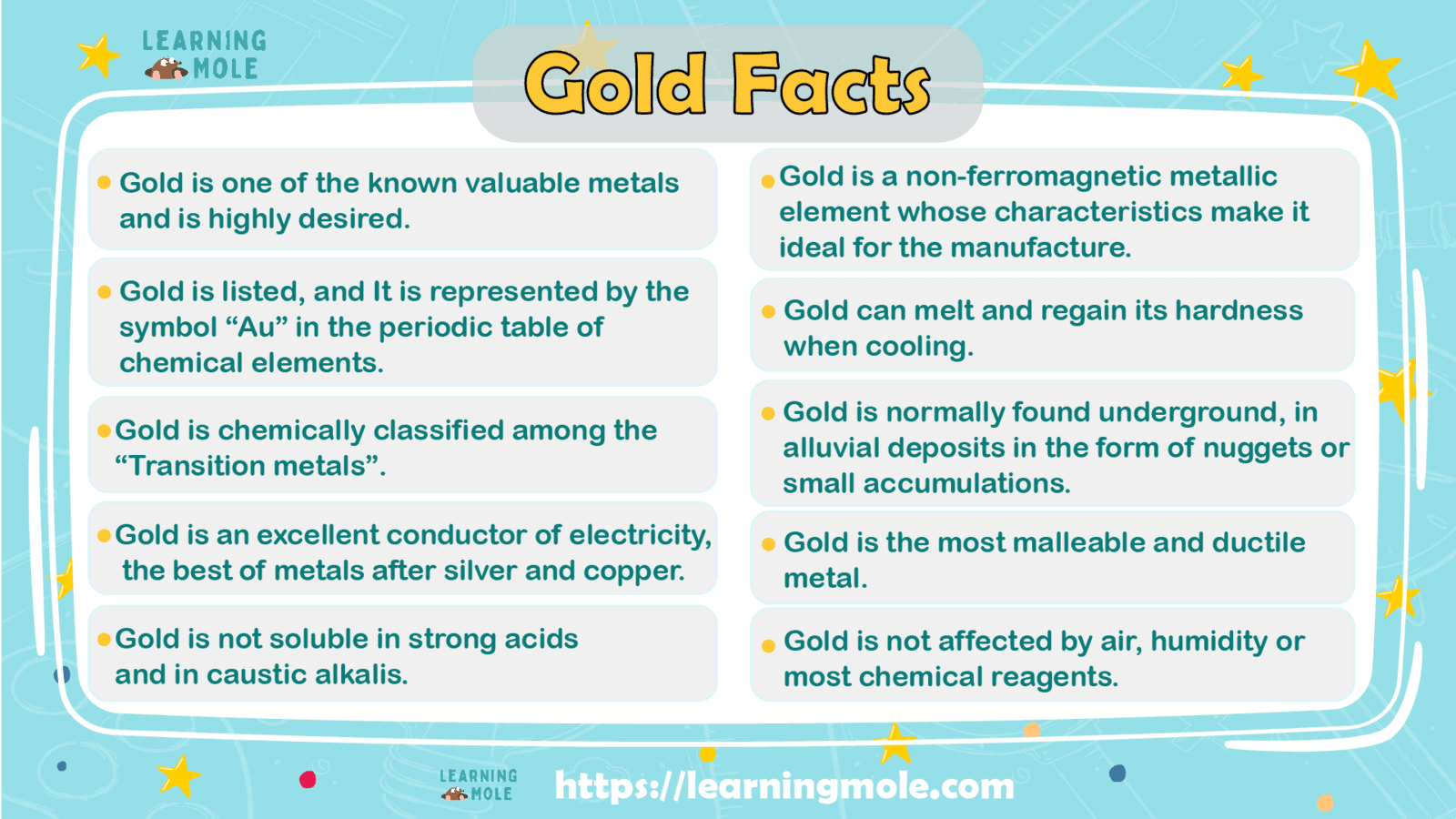
Gold is one of the known valuable metals and is highly desired.
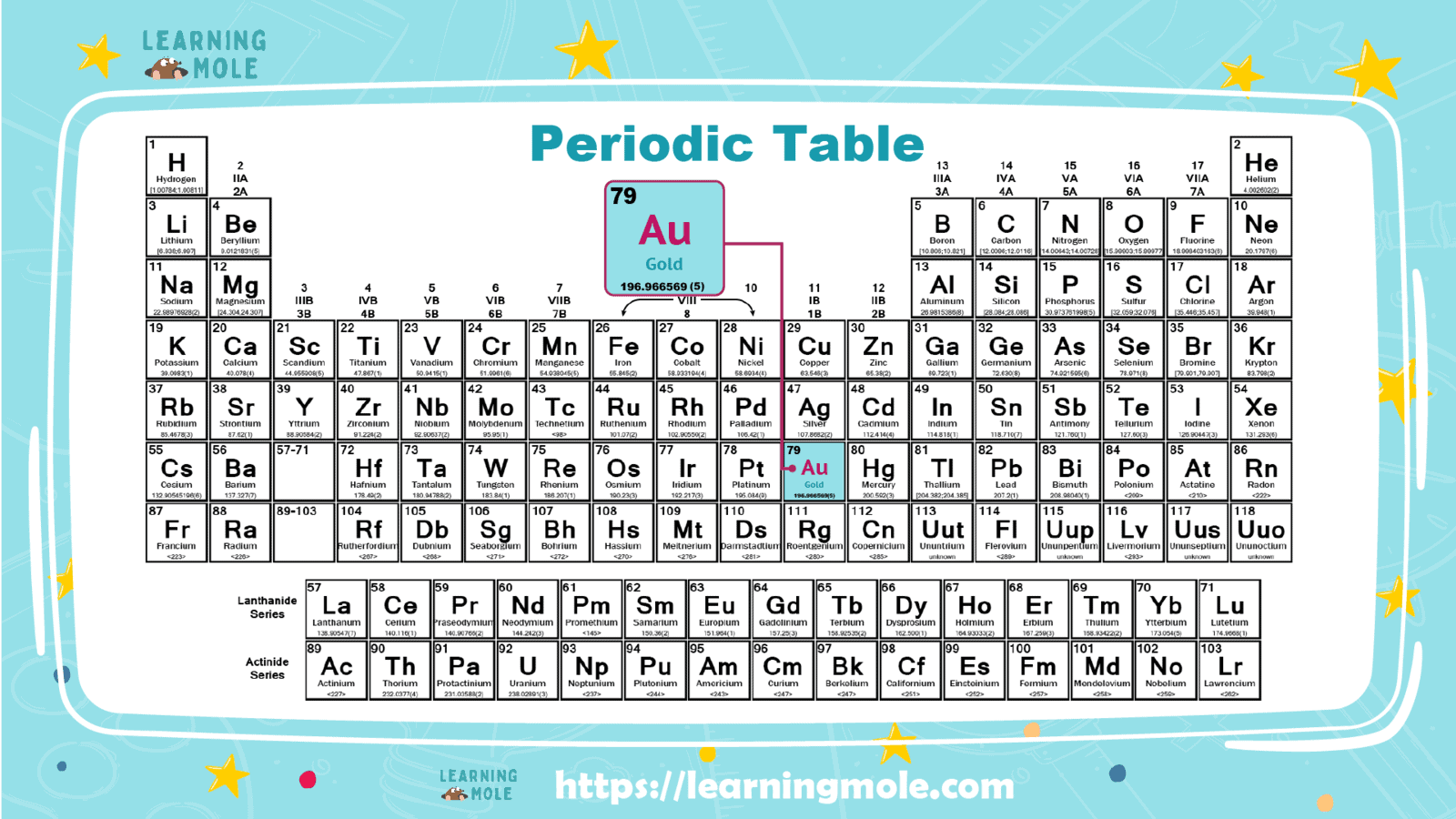
It is listed, and It is represented by the symbol “Au” in the periodic table of chemical elements. It is also a slightly reactive element, chemically classified among the “Transition metals”.
Gold is a non-ferromagnetic metallic element whose characteristics make it ideal for the manufacture of different types of objects since it can melt and regain its hardness when cooling.
Gold is normally found underground, in alluvial deposits in the form of nuggets or small accumulations, both in its pure state and together with other minerals in alluvial formations, which are sought and exploited by mining.
The yellow metal has physical and chemical properties that make it unique. In nature, these characteristics are as follows:
- Gold is the most malleable and ductile metal: one gram of gold can be hammered into plates with an area equal to one square metre. These very thin sheets of pure gold are used to decorate picture frames, mirrors, etc. It is a soft metal, and to give it greater mechanical strength, it is alloyed with other metals.
- Gold is not affected by air, humidity or most chemical reagents. It is not soluble in strong acids (hydrochloric, nitric and sulfuric) and in caustic alkalis; instead, it can be oxidized by aqua regia (a mixture of hydrochloric and nitric acids with a 1:3 ratio) or with aqueous solutions containing sodium or potassium cyanide in the presence of oxygen or hydrogen peroxide. In aqua regia, it forms tetrachloroauric acid (HAuCl4). In contact with mercury, it melts in it, forming an alloy called amalgam.
- Gold is alloyed with many other metals: alloys with copper are reddish, with iron green, with aluminium purplish, with platinum white, bismuth and silver blackish.
The most frequent oxidation states of gold are +1 and +3. Gold ions are easily reduced by adding any other metal. The added metal oxidizes and melts, causing the metallic gold to precipitate.
It is an excellent conductor of electricity, the best of metals after silver and copper.
The chemical composition of gold:
The metal is chemically composed of the element gold and often contains varying amounts of silver (up to 40%), as well as iron, lead and bismuth.
Gold is the 3rd element in the 11th column of the periodic table. It is classified as a transition metal. Gold atoms contain 79 electrons and 79 protons, with 118 neutrons in the most common isotope.
Gold that contains high amounts of silver (from 20 to 40%) is known as electrum. The metal melts easily at its melting point (1064.43 °C) and boils at the boiling point between 2600 °C and 2807 °C.
chemical properties of gold
Atomic number: 79
Atomic mass: 196.967
Melting point: 1064.43 degrees Celsius
Boiling point: 2807 degrees Celsius
Density: 19.32 g/cm3
Parity: 3,1
Electron distribution: Xe [4F14.5d10.6S1]
Gold is a metal that is not chemically active, and therefore it does not oxidize, not rust, is not affected by most acids, and does not dissolve in various acids; however, it dissolves in aqua regia (a mixture of nitric acid and hydrochloric acid aqua rgia).
It is an excellent conductor of heat and electricity, and only silver and copper surpass it in the property of conducting electricity heat, but it resists weather factors unlike these two metals, so it is an ideal element in the field of electronics.
It is considered a heavy metal and is almost twice as heavy as iron, so one cubic meter of pure gold weighs more than 20 tons.
Pure gold is a soft and easy metal, as it can be hammered and spread in the form of a sheet the thickness of a part of a micron, and a micron is a part of a millionth of a meter. A wire with a length of three kilometres without interruption.
- An inactive element means that it does not decompose, has no chemical activity, and cannot be used in chemical reactions.
- Good conductor of electricity.
- The yellow metal is rare and has a soft texture.
- Electro-negativity of yellow metal on the Pauling scale (2.4).
- The van der Waals radius is 0.144 nano-meters.
- It includes seven isotopes.
- The first ionization energy of the yellow metal is (888) kJ mol 1-.
- Its second ionization energy is (1976.6) kilojoules 1-.
- Atomic number (79).
- The atomic mass is more than 196 grams per 1 mol.
Colours of Gold
Gold jewellery is a mixture of metals and not pure yellow metal, as the jewellery is mixed with copper, palladium, silver, zinc and platinum in order to create various colours of the yellow metal. The most common colours of gold are as follows:
Yellow colour:This colour is produced when pure yellow metal is mixed with zinc, copper and silver. It is considered one of the purest and most sensitive colours, but it requires less maintenance than all other metal colours.
White gold: is a mixture of yellow metal and platinum or palladium. White gold can also consist of yellow metal and palladium with zinc and nickel. This colour is scratch-resistant and more solid, and its price is reasonable compared to other colours.
Rose gold: This colour consists of a mixture of yellow metal, silver and copper, and this type is the most expensive of the other colours, and the pink colour of the yellow metal is characterized by being the most durable.
Green gold: is a mixture of yellow metal and silver, and sometimes copper is added to it. Silver is responsible for giving the metal a green colour, or what is called (electrum).
Gold extraction and production
The process of mining the yellow metal means the exploration of the yellow metal to extract it from the mines, based on advanced modern technologies.
Its mining process is a global business that takes place in all continents of the world except Antarctica, and the yellow metal is obtained and extracted from mines in various sizes and different types.
Gold prospecting and mining
Exploration of yellow metal and mining increased significantly geographically, as for four decades, the vast majority of yellow metal production came from South Africa, but during the recent period, specifically in 2016, China was the largest gold-producing country in the world.
Where China’s production is estimated at 14% of the total annual global production, while Asia as a whole produces 23% of gold. As for South and Central America, the total production amounts to 17% of the total annual global production, while North America has an output of about 16%. 19% of global production is from the continent of Africa.
Gold extraction and purification stage
Most of the yellow metal mining and extraction processes are carried out through the cyanide process, in which the yellow metal is oxidized in an alkaline cyanide solution.
After the completion of the yellow metal analysis process, the solids are separated from the rich solution, and the cyanide process is carried out through the use of basin filtration, and the solvents are kept in large tanks that include engines.
To obtain the yellow metal and extract it from low-quality ores, heap filtration work is done, then huge piles of dilute sodium cyanide solution are sprayed, then the solution begins to seep through the piled ore, and the yellow metal begins to dissolve.

Uses of Gold
Its role in human society is important, as it is a symbol of wealth, power and vanity, as well as glory and triumph.
That is why it has been used for national trophies, jewels and emblems or to back up different countries’ currencies, the value of which was initially measured by the gold reserves of that country’s Central Bank.
Gold has been used for thousands of years to make jewellery and coins. Today it is still used for jewellery. Gold is also an important and reliable investment.
When gold is used as jewellery or for coins, it is generally not pure gold. Pure gold is called 24-karat gold, and it is very soft. Typically, gold is made with other metals, such as copper or silver, to make it more solid and durable.
The yellow metal was used in the past in the manufacture of pharaonic masks, and the pharaohs used it in the manufacture of coffins for rulers, as it was used in the manufacture of artwork; in addition to that, it was used in the manufacture of coins more than 6000 years ago.
In modern times, yellow metal is used in the manufacture of jewellery and jewellery, as it is more than 78% of gold. It is used in the manufacture of jewellery. It is also used in dressing teeth and making fillings due to the hardness and durability of the yellow metal.
The yellow metal is used in the treatment of some diseases such as (cancers), where radioactive (gold) is used in the treatment of cancer, while the yellow metal solution is used in the treatment of rheumatism and osteoarthritis, and it is also added in some cosmetic creams.
The yellow metal is used to cover small internal parts of spacecraft, to moisturize mechanical parts, and is used in helmets for space suits, as it works to protect against heat and infrared radiation.
Gold is heavily used in the electronics industry because of its good electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance. Numerous connections and electrical contacts are gold-plated for protection and reliability.
Other applications for gold include heat protection, dental work, and decoration such as gold thread and gold plating.
The Economic role of Gold
The yellow metal had a prominent and major role in the US economy, and the impact of the yellow metal on the economy began to decline and fade depending on the strength of other investments.
Whereas at a time when risks increase around other investments, the yellow metal appears to be the safest means, and through the price of the yellow metal, the economic situation is identified when the United States of America relies on the (gold) standard.
During the recent period, global yellow metal prices witnessed a general state of instability in conjunction with the Corona pandemic that the world is facing.
And the demand for yellow metal is supported by many factors, such as its consumption as jewellery and jewellery and its use by central banks as reserve assets that protect it against various market risks.
These factors increase the demand for yellow metal in all economic conditions, which makes yellow metal occupy the status of a safe asset, and countries use it as a stockpile that is resorted to in times of inflation and economic crises.
Interesting facts about Gold
Where on Earth are they located?
Gold is a scarce element on Earth. Because it does not interact with many other elements, it is often found in its original form in the Earth’s crust or mixed with other metals such as silver. It can be found in underground veins or in small portions in sandy riverbeds.
Gold is also found in ocean water. However, the process of recovering gold from ocean waters costs more than the gold itself.
Gold Toxicity
Pure gold is basically harmless. However, it is not impossible to witness cases of moderate allergies to this metal. But being so little reactive, it does not represent a danger in itself, but in the composition of toxic salts such as gold chloride (AuCl 3).
Related Articles:
- Platinum: All you need to know about the Strong element
- Copper: Properties, Uses, Reactions and more
- Mercury: Many debates about the valuable Element
Why not subscribe to our LearningMole Library for as little as £1.99 per month to access over 1200 fun educational videos.


Leave a Reply