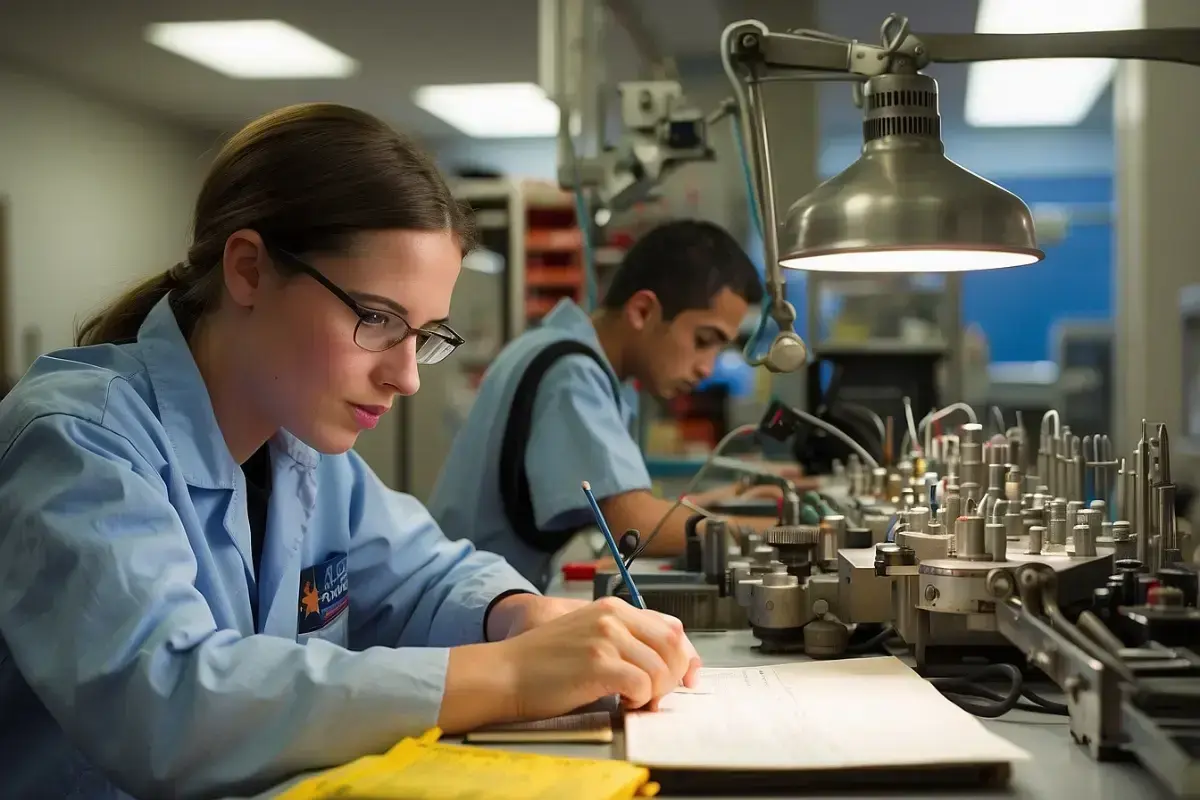

Beyond Doctors and Astronauts: A World of Career Possibilities
Table of Contents
When we look to the stars and dream of the infinite possibilities they represent, we often think of astronauts heroically venturing into space or doctors pushing the boundaries of medical science to keep them healthy. However, the universe of careers in the space industry extends far beyond these prominent roles. Opportunities in space exploration and related fields are blossoming, offering a vast array of jobs that combine science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) with innovation and creativity.
These careers are not just for those with advanced degrees in aerospace engineering or astrophysics. The evolving space sector requires a diverse range of skills and backgrounds. From innovators who design sustainable habitats for life beyond Earth to educators who inspire the next generation of space explorers, space-related careers encompass a wide spectrum. Agencies and organisations across the globe are actively seeking individuals with a passion for exploration and a drive to address the unique challenges that arise when we step off our home planet.
The Spectrum of Space Careers

Exploring space offers a vast array of career opportunities beyond the well-known roles of doctors and astronauts. Each role contributes to the complex tapestry of the space industry, from crafting cutting-edge technology to supporting the critical operations of missions.
Astronauts Selection and Training
Astronauts are synonymous with space exploration, and their selection and training are rigorous and multifaceted. To become an astronaut, candidates undergo extensive physical and psychological testing. Training spans survival training, scientific research skills, and learning to operate spacecraft. The backgrounds of astronauts are diverse, including engineers, scientists, and even educators, each bringing unique expertise to space missions.
Engineering and Robotics
Engineers and robotic experts are pivotal in advancing space technology. They design and build spacecraft, space rovers, and intricate onboard systems that ensure missions can be conducted safely and effectively. From aerospace engineers to robotics control technicians, these professionals face unique challenges, such as creating technology that functions in the harsh conditions of space.
Research and Development
Research and development form the backbone of space exploration, prompting advancements that trickle down to numerous sectors. Specialists in this field may engage in developing new materials for space suits or innovating propulsion methods that could redefine space travel. Their work often involves collaborating with educational institutions and space agencies, contributing to scientific knowledge and potential commercial applications.
Mission Control and Support
Behind every successful space mission is a diligent team of mission control personnel. These professionals monitor spaceflights, attend to the well-being of astronauts, and manage unexpected challenges. Mission support roles also include the strategists and planners who meticulously chart out each phase of the mission, ensuring objectives are met and the safety of crew and equipment is upheld throughout.
The space industry encompasses a multitude of careers that are integral in shaping the future of space exploration. Whether you’re fascinated by the mechanics of spacecraft engineering or the strategic complexities of mission control, the universe of space careers has a trajectory for everyone.
Emerging Fields in Space Exploration

The universe of space careers is expanding with new and exciting fields. Beyond the traditional roles we may think of, there are unique specialities emerging that play crucial roles in the advancement of space exploration.
Space Medicine
Space medicine is a critical interdisciplinary field that combines elements of healthcare and space technology to support the health and well-being of astronauts during space travel. Advances in this field are essential for deep space exploration, where astronauts face unprecedented physical and psychological challenges. Technologies are developed to facilitate distance medicine, potentially offering remote guidance for in-flight medical procedures.
Astrobiology
Astrobiology delves into the origins, evolution, and future of life in the universe. With space agencies aiming for missions to Mars and other celestial bodies, understanding the potential for life in extreme environments is vital. Astrobiologists not only study life’s tenacity on Earth but also develop techniques to search for biosignatures on other planets.
Space Law and Ethics
The field of space law and ethics is increasingly relevant as space travel becomes more commercialised. Topics such as the peaceful use of space, space debris management, and the rights of space-faring entities are at the forefront of discussions. Legal frameworks ensure that space exploration is conducted responsibly, respecting international treaties and the protection of celestial bodies.
Emerging careers in space extend far beyond the cockpit of a spacecraft. Whether in medicine, biology, or law, each new field allows us to safely and ethically push the boundaries of what humanity can achieve among the stars.
The Role of Agencies and Organisations

The expansion and success of space endeavours are largely influenced by a network of agencies and organisations. These entities are integral in shaping careers beyond doctors and astronauts, covering a multitude of disciplines and responsibilities.
NASA’s Endeavours
NASA, the front-runner in the space exploration arena, not only spearheads missions to outer space but also contributes significantly to the development of careers that support these missions. Efforts include those at the International Space Station (ISS), where international collaboration and a variety of careers come to life. NASA’s initiatives provide a plethora of opportunities, with roles that range from engineering and science communication to mission operations and support services.
International Space Collaboration
Collaboration among global space agencies elevates the collective ability to undertake ambitious space programmes. Beyond NASA, agencies like the European Space Agency (ESA), the Russian Space Agency (Roscosmos), and others contribute to both the ISS and various exploration projects. These collective endeavours not only require astronauts but also a robust support system made up of researchers, technicians, and administrative professionals, all funded by international agreements and the sharing of resources.
Private Sector Contributions
The private sector plays an increasingly essential role in space exploration. Companies like SpaceX and Blue Origin are forging paths to the stars, with funding and innovation fuelling a new era of space travel. Their contributions offer careers in spacecraft design, launch services, and even the burgeoning industry of space tourism. These private entities create jobs that support construction, operations, and customer experience, thereby diversifying the universe of space-related careers.
Exploring the cosmos has transcended the roles traditionally ascribed to doctors and astronauts. Now, you could be a part of an exciting network of professionals across various agencies and organisations that make space exploration possible. Whether through contributions to NASA, international partnerships, or innovative private-sector initiatives, the opportunities in this thrilling field are truly out of this world.
Space Science and Technological Advancements

In the realm of space exploration, scientific achievements and technological innovations continue to push the limits of what’s possible, unveiling new career paths far beyond the traditional roles of doctors and astronauts.
Ground-breaking Discoveries
The field of space science is constantly making ground-breaking discoveries that challenge our understanding of the universe. From uncovering the mysteries of dark matter to the detection of Earth-like exoplanets, these developments not only captivate the scientific community but also expand the horizon for potential careers in research and analysis. Through such discoveries, the human research programme evolves, focusing on the effects of space travel on astronauts and opening doors to new scientific roles dedicated to safeguarding human health in space.
Innovation in Space Technology
Innovation in space technology is at the forefront of enabling deeper space exploration. Recent advancements have seen the development of powerful rockets capable of reaching Mars, space habitats for long-duration missions, and robotic rovers for planetary exploration. These technologies derive from concerted efforts in engineering, computer science, and physics, illustrating the diverse career opportunities spanning from scientific research to operational support. Innovations like reusable spacecraft are not only scientific marvels but also testaments to human ingenuity.
The relentless pursuit of knowledge in space science and the continuous evolution of space technology provide a universe of career opportunities that go beyond what we traditionally associate with space exploration. With new findings and technologies regularly emerging, those with a passion for science and innovation can find their place in the ever-expanding cosmos of space careers.
Human Factors in Space Travel

When we talk about the vast expanse of space and our journey through it, we often focus on the technical aspects. But at the heart of space travel are the humans who make the journey. The challenges faced by our bodies and minds in such an alien environment are profound and require careful consideration and standard measures to ensure the safety and well-being of astronauts.
Physiological Considerations
Understanding the physiological impacts of space travel on the human body is crucial. In the weightlessness of space, muscles and bones can weaken, a condition known as muscle atrophy and bone density loss. Space agencies have to implement rigorous exercise regimens to combat these effects. Also, without Earth’s protective atmosphere, astronauts are exposed to higher levels of radiation, which could lead to increased health risks such as cancer. Therefore, spaceflight-standard measures need to address these heightened risks through shielding and monitoring.
Psychological and Behavioural Aspects
The psychological well-being of astronauts is just as important as their physical health. Confined spaces, isolation from loved ones, and the pressure of working on critical missions can have significant effects on an astronaut’s mental health. To support the crew’s behaviour and well-being, space programmes include thorough training in conflict resolution, regular communication with loved ones, and even the inclusion of leisure activities. As we prepare for future human exploration beyond our current frontiers, identifying and managing these challenges becomes increasingly important for mission success and the exploration of new worlds.
Training for Space Missions
In the realm of space exploration, training for missions is a multi-faceted operation, requiring intense preparation in both physical and cognitive domains to ensure astronauts can thrive in off-world environments.
Simulated Environments
Simulated environments are a cornerstone of astronaut training, meticulously designed to emulate the challenges of space. These simulations can take place in analogue habitats or virtual reality, providing a realistic setting where astronauts can practise daily living and emergency scenarios. Programmes often include mission-specific simulations that focus on enhancing sensorimotor adaptation to microgravity and testing adaptability to unexpected changes.
Physical and Cognitive Preparedness
Consistent exercise is paramount in an astronaut’s regimen to counteract the effects of living in a microgravity environment. Astronauts engage in daily workouts using specialist equipment designed to maintain cardiovascular health, muscle mass, and bone density. Alongside physical training, cognitive preparedness is honed through tasks that test critical thinking, spatial awareness, and decision-making under pressure. Tailored to enhance cognition, these exercises help astronauts develop the mental acuity necessary for the complexities of space missions.
Living and Working in Space
Living and working in space presents an array of challenges and requirements that drastically differ from those on Earth. Due to the unique environment of space, particularly in habitats like the International Space Station (ISS), both the human body and the technologies we rely on must adapt to conditions such as microgravity and the need for autonomous life support systems.
Microgravity Challenges
In the microgravity environment of space, the human body experiences various changes, some of which can affect muscle and bone density. Prolonged exposure to zero-gravity conditions can lead to muscle atrophy and decreased bone density, which is why astronauts aboard the ISS are required to engage in daily exercise routines. These routines are essential for counteracting the adverse effects of living in space for prolonged periods, especially in preparation for the return to Earth’s gravity.
Astronauts also utilise special equipment designed to work in microgravity. This includes exercise devices like the Advanced Resistive Exercise Device (ARED), which simulates weightlifting on Earth, helping to preserve muscle strength and bone density.
Life Support and Habitability
Life support systems on space missions are integral to ensuring that astronauts have access to fresh air, clean water, and adequate food supplies. Life support systems must function autonomously, recycling vital resources to maximise efficiency and reduce the need to take large quantities of supplies on long-duration missions. On the ISS, for instance, water recovery systems are able to recycle about 90% of the water used on board.
Habitability encompasses more than just survival needs; it includes creating a comfortable and psychologically sustainable environment for astronauts. This means considering factors like personal space, noise levels, and avenues for relaxation and leisure activities. The design of living quarters in space habitats must strike a balance between practicality and comfort to support mental well-being.
When discussing living and working in space, such as in the unique environment of the ISS or during long-term spaceflight, it becomes clear that both the human body and technology must be finely tuned to these conditions. Ensuring the proper function of life support systems and the habitability of space environments is crucial for the success and health of astronauts.
Space Exploration Milestones

Space exploration milestones have revolutionised our understanding of what lies beyond Earth. From stepping on the moon to planning missions to Mars, humanity’s quest into the cosmos continues to achieve the extraordinary.
The Moon and Mars Missions
The Moon has been a focal point of space exploration. In 1969, the historic Apollo 11 mission made headlines as humans walked on the moon for the first time. This monumental achievement set the bar for all future endeavours. Since then, various missions have aimed to unlock the moon’s secrets, with plans for establishing a lunar base as a stepping stone for deeper space exploration.
Mars, known as the Red Planet, has captivated the attention of space agencies worldwide. Notable missions like NASA’s Mars Rover have roamed its surface, searching for signs of past life and paving the way for human exploration. The concept of manned missions to Mars is becoming more tangible, with ambitious projects like Mars One attempting to turn science fiction into reality and establish a permanent human settlement on Mars.
Interstellar Objectives
Interstellar exploration might seem distant, but significant objectives have been set to reach beyond our solar system. While scientists and engineers work on technologies to travel to and possibly inhabit other planets, robotic probes like Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 have become our eyes and ears, sending invaluable data from the far reaches of space.
In terms of interstellar communication, projects like Breakthrough Starshot aim to develop spacecraft capable of journeying to our nearest stellar neighbours, with the objective to photograph and document planets in the Alpha Centauri system. Instruments aboard these missions could provide insights into the possibility of life beyond our solar system.
Remember, space exploration isn’t just about reaching new worlds; it’s about the journey, the technology, and the boundless curiosity that propels us forward. Have you ever gazed at the night sky and wondered about stepping on the moon or walking the red terrain of Mars? You’re not alone in your curiosity – these missions fuel the imaginations of teachers, parents, and children alike, encouraging the next generation to dream big and look up.
Health and Safety in Outer Space
Ensuring the health and safety of people in outer space is crucial due to unique challenges not present on Earth. The absence of gravity, exposure to radiation, and the potential for microbial threats are considerable risks to human health, including the immune system and increased cancer risk.
Radiation and Microbial Threats
In outer space, astronauts are exposed to elevated levels of cosmic radiation, which can increase the risk of health disorders, including cancer. To protect the delicate balance of the body’s microbiome, which can be affected by this radiation and the confined spaces of spacecraft, countermeasures such as shielding materials are essential.
There’s also the threat of microbial contamination. Spacecraft are sterile environments, but the long-term presence of humans can introduce new microbial threats. The immune system may operate differently in space, so monitoring the health of the microbiome is vital for the well-being of astronauts.
Medical Interventions and Countermeasures
Medical interventions in space depend on thorough pre-flight health checks, onboard medical expertise, and protocols for dealing with medical events. Astronauts receive training in medical procedures, and telemedicine allows for consultation with experts on Earth.
To counter the health risks posed by radiation, various countermeasures are used, from medicinal therapies to fortify the body to advanced technologies in spacecraft construction. The aim is to ensure astronauts remain as safe as possible from the moment they leave Earth’s atmosphere until their return.
Future of Interplanetary Settlements

As humanity ventures beyond Earth, the concept of interplanetary settlements has shifted from science fiction to potential future reality. These settlements, which encompass humans living in fully habitable structures beyond our planet, represent a significant leap in space exploration and habitation.
Extraterrestrial Habitats
The development of extraterrestrial habitats on the Moon, Mars, and potentially other celestial bodies is crucial for safe and sustainable long-term human habitation. These habitats would need to provide life support systems that offer air, water, food, and protection from harsh environments. The design of these structures is complex, as they must withstand the challenges of lunar orbit and the vacuum of space while maintaining Earth-like conditions inside. Researchers and engineers are exploring innovative approaches, such as using regolith—the soil-like material on the Moon and Mars—to create building blocks for settlement structures.
The Potential for Human Colonisation
Human colonisation of other planets rests not just on the feasibility of interplanetary travel but on the ability to create self-sustaining settlements. This involves not only technological prowess but also careful consideration of the psychological and sociological aspects of long-term space habitation. For colonisation to be successful, the fundamental needs of a society must be met, ranging from physical health care to recreational spaces. The concept envisions a future where daily life in a settlement outside Earth offers comparable freedoms and quality of life, which will require meticulous planning and continuous innovation.
Innovations in Space Education

The landscape of space education is evolving with innovative approaches designed to inspire and equip the next generation of explorers. These initiatives leverage technology and the principles of STEM to create dynamic learning environments.
STEM Initiatives
STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) initiatives are at the forefront of educational innovation. They offer students the opportunity to engage directly with the real-world applications of their studies. Programmes now commonly include robotics and coding, where pupils can create tangible examples of their learning, stimulating their natural curiosity and problem-solving skills. For instance, teaching resources from LearningMole offer engaging content focused on STEM disciplines, allowing young learners to discover and explore in an interactive manner that aligns with their intuitive learning styles.
Virtual Learning Experiences
Equally transformative are the advancements in virtual learning experiences. Through the use of virtual reality, students are no longer limited to the walls of a classroom; they can embark on a virtual field trip to the International Space Station or the surface of Mars. This immersive use of technology not only brings complex space concepts to life but also encourages a deeper understanding by placing students in the heart of the action. Learning experiences become vivid and memorable, solidifying the educational impact in a way traditional methods may not.
Virtual platforms also support the varied requirements of learners, including those with special educational needs. The accessibility and customisation features of online learning tools mean that education can be more inclusive than ever before, a principle that LearningMole champions.
Frequently Asked Questions

Exploring a career in space exploration opens up a realm of possibilities beyond the more commonly known roles of doctors and astronauts. In this section, we’ll address some of the most commonly asked questions about the diverse career paths available in this field.
What are some exciting career paths in space exploration beyond the usual roles we hear about?
Beyond the roles of astronauts and medical physicians, careers in space exploration include space scientists, satellite engineers, mission planners, astrobiologists, and space policy analysts. These professionals contribute to our understanding of space and the development of missions that push the boundaries of human knowledge.
Can you list various professions related to astronomy and space studies?
Certainly! Professions related to these fields include astrophysicists, planetary geologists, radio astronomers, space weather experts, observational astronomers, and spacecraft designers. Each role plays a crucial part in interpreting celestial phenomena and advancing space technology.
What qualifications are needed for employment at NASA in various capacities?
Employment at NASA requires qualifications that are role-specific, ranging from a bachelor’s degree in engineering, physical science, biological science, computer science, or mathematics to advanced degrees for more specialised positions. Candidates must also possess relevant experience and a strong foundation in their field of expertise.
How can one utilise satellite technology in different career fields?
Satellite technology has myriad applications across different career fields, including environmental monitoring, climate research, telecommunications, navigation, and geospatial analysis. Careers in these areas often involve data analysis, software development, and systems engineering to harness satellite data for practical uses.
What are some space industry careers that don’t heavily involve mathematics?
Not all space industry careers require heavy use of mathematics. Roles such as science communicators, space historians, legal consultants specialising in space law, and administrative staff in space agencies like NASA are essential to the industry and do not focus predominantly on mathematics.
Could you tell me about the types of jobs that exist at NASA and their corresponding salary ranges?
NASA offers a wide range of jobs, from engineering and scientific roles to administrative and support positions. Salaries at NASA vary widely, with entry-level positions often starting from the GS-7 pay grade and senior positions reaching GS-15 or higher, which could range from approximately $40,000 to over $130,000 annually, depending on experience and qualifications.


Leave a Reply