
Fun Vikings Facts for Kids – KS2
You know the Vikings that fought battles and raided lands but what else do you know? Let’s have a look at some Vikings Facts that you may not have known.
Table of Contents
- Where Did the Vikings Come From?
- Culture: What Was It Like to Be a Viking?
- Vikings Facts: Clothing
- Viking Facts: Burials
- Viking Facts: Past-Times
- Vikings Facts: Longships
- Vikings Facts and Myths
Where Did Vikings Come From?
All the stories tell us that they came from all around Scandinavia, such as Sweden, Denmark, and Norway. (Where Norway, Sweden, and Denmark are today). They sent armies to Britain about the year 700 AD to take over some lands, and they lived here until around 1050. They settled in the British Isles and what is now known as northern France. The Norse that settled in northern France broke from their brothers and became known as Normans.
The majority of Vikings were farmers. They grew grain crops, like barley, rye, or oats. They would make bread from grain. As the leading mariners of their time, Vikings employed state-of-the-art boat-building technology. One of their signature inventions was the longship, a wooden boat with a shallow-draft hull and one long row of oars along each side. While these people are often attributed as savages raiding the more civilized nations for treasure and women, the motives and culture of the Viking people are much more diverse. These raiders also facilitated many changes throughout the lands from economics to warfare.
Culture: What Was It Like to Be a Viking?
We find that most people believe that the Vikings were soldiers, raiders, and pillagers. They think the Vikings just sailed around the world in longships and rowed from town to burn houses and steal gold. This is not entirely accurate, and this belief exaggerates only one single part of Norse life. But we must know that Vikings were farmers, traders, travellers, hunters, trappers, fishers, and artisans. Viking women were skilled weavers and textile makers.
Vikings Facts: Clothing
Clothes were primarily made of wool, linen, and animal skins. Women would turn wool into yarn or fabrics and then dye them to give them colour. Women would have used a weaving loom to make clothing.
Clothing showed status
When the Norse gained more wealth and power, they began to embellish their clothes. Viking clothes were primarily used for warmth and protection, but they were also used to show off status. Rich Vikings would have worn clothes made from silk or with silk stitching and embroidery because this material was associated with wealth. Different colours also indicated power and prestige. Wealthy Vikings would have worn bright blue colours to show their place in society.
Brooches
Brooches were used to fasten shawls, cloaks and the straps of Viking women’s dresses. Brooches were also used for decorative purposes. Brooches came in various different sizes and shapes, for example Vikings had trilobite brooches and shell-shaped brooches and their brooches were made from gold, bronze and silver. Viking women often wore strings of beads made from glass between the brooches for decoration. Pins made from wood, bone or gold were also used to hold cloaks in place.
Waterproof Clothing
Vikings lived in cold and wet environments meaning their clothing had to keep them warm and dry. The Vikings clothing was made from wool and fur to keep them insulated from the harsh weather. The Vikings also made their clothing waterproof. They used skin that was treated with beeswax and fish oil in order to make their clothing waterproof. Leather would have also been a waterproof material they used.
Children Clothing
Viking children would have worn similar garments to their parents. Viking boys would have worn pull-on tunics made of wool and baggy trousers held up by a drawstring. In the colder weather they would have worn a cloak and a cap made of wool and fur. Viking boys would have also worn leather belts with a knife holder and a purse attached to hold things in. Viking girls would have worn a loose ankle-length dress tied with ribbons or draw-strings and an apron over it. To keep warm, they would have worn a shawl or cloak and bonnet on their head. All clothes would have been handmade.
Vikings Didn’t Wear Horned Helmets?
Vikings didn’t wear horned helmets. Forget almost every Viking warrior costume you’ve ever seen. Sure, the pugnacious Norsemen probably sported headgear, but that whole horn-festooned helmet look? Depictions dating from the Viking age don’t show it, and the only authentic Viking helmet ever discovered is decidedly horn-free. Perhaps the horned helmets were inspired by descriptions of northern Europeans by ancient Greek and Roman chroniclers.

Vikings didn’t wear horned helmets. Forget almost every Viking warrior costume you’ve ever seen.
Viking men spent most of their time farming
This may come as a disappointment, but most Viking men brandished scythes, not swords. True, some were callous pirates who only stepped off their boats to burn villages, but the vast majority peacefully sowed barley, rye, and oats—at least for part of the year. They also raised cattle, goats, pigs, and sheep on their small farms, which typically yielded just enough food to support a family.
Viking men spent most of their time farming. Vikings would have used their animals for food and for clothing. When they didn’t have enough food to feed the animals, they would kill them and preserve them in salt. Viking men would have also gone fishing and taught their sons how to catch fish. The most demanding physical work, such as building houses and ploughing were done by slaves.
Vikings Facts: Burials
Just like how today different cultures have different burial rituals, the Vikings also buried their dead in different traditions to those around the world at the time. Let’s have a look at some things that the Viking did for their burials.
Vikings buried their dead in boats
There’s no denying Vikings loved their boats—so much that it was a great honour to be interred in one. In the Norse religion, valiant warriors entered festive and glorious realms after death, and it was thought that the vessels that served them well in life would help them reach their final destinations. Distinguished raiders and prominent women were often laid to rest in ships, surrounded by weapons, valuable goods, and sometimes even sacrificed slaves.
Viking women were buried with valuables that reflected their status
Depending on where a Viking woman ranked in society or what role she played, she would’ve been buried with objects to reflect her life. If a Viking woman was of importance, she would have been buried with luxuries such as oil lamps or knives. Many Viking women also had keys buried with them to reflect their status as housewives. Objects that have been found in Viking women’s graves have been textiles, various brooches, sickles, beads and rings.
Some burial ships would be set alight
Sometimes the ship containing the body was set alight on funeral pyres. In many movies and books, we see this as the main way that Vikings would have been laid to rest, however, this was only done for Vikings of high honour, and it was done to speed up the journey to the afterlife.
Vikings Facts: Past Times
Vikings Skied for Fun
Scandinavians developed primitive skis at least 6,000 years ago, though ancient Russians may have invented them even earlier. By the Viking Age, Norsemen regarded skiing as an efficient way to get around and a popular form of recreation. They even worshipped a god of skiing, Ullr.
Vikings Played Board Games
When Viking men and women weren’t farming or hunting, they would’ve played many board games, such as hnefatafl, which is known as Viking chess. It is pronounced as “neffa-taffle”. You can see a Viking chess set at the British Museum. The Viking chess set that was found is called the Lewis Chessmen. It was named after the area where it was found, which was Isle of Lewis in Scotland. Lewis was densely populated with Vikings in the past. The Lewis Chessmen were carved from whale teeth and walrus ivory.
Vikings were Great Story Tellers
Telling stories was a huge part of a Vikings life. By telling stories, Vikings educated their descendants about Viking culture, history and faith so that they could then pass it on to future generations. Storytelling was how Vikings kept legacy alive before they began writing things down. Vikings often told stories around the fire. Vikings called skalds recited epic tales aloud, to honour heroes and legends of Viking history.
Vikings Facts: The Viking Ships
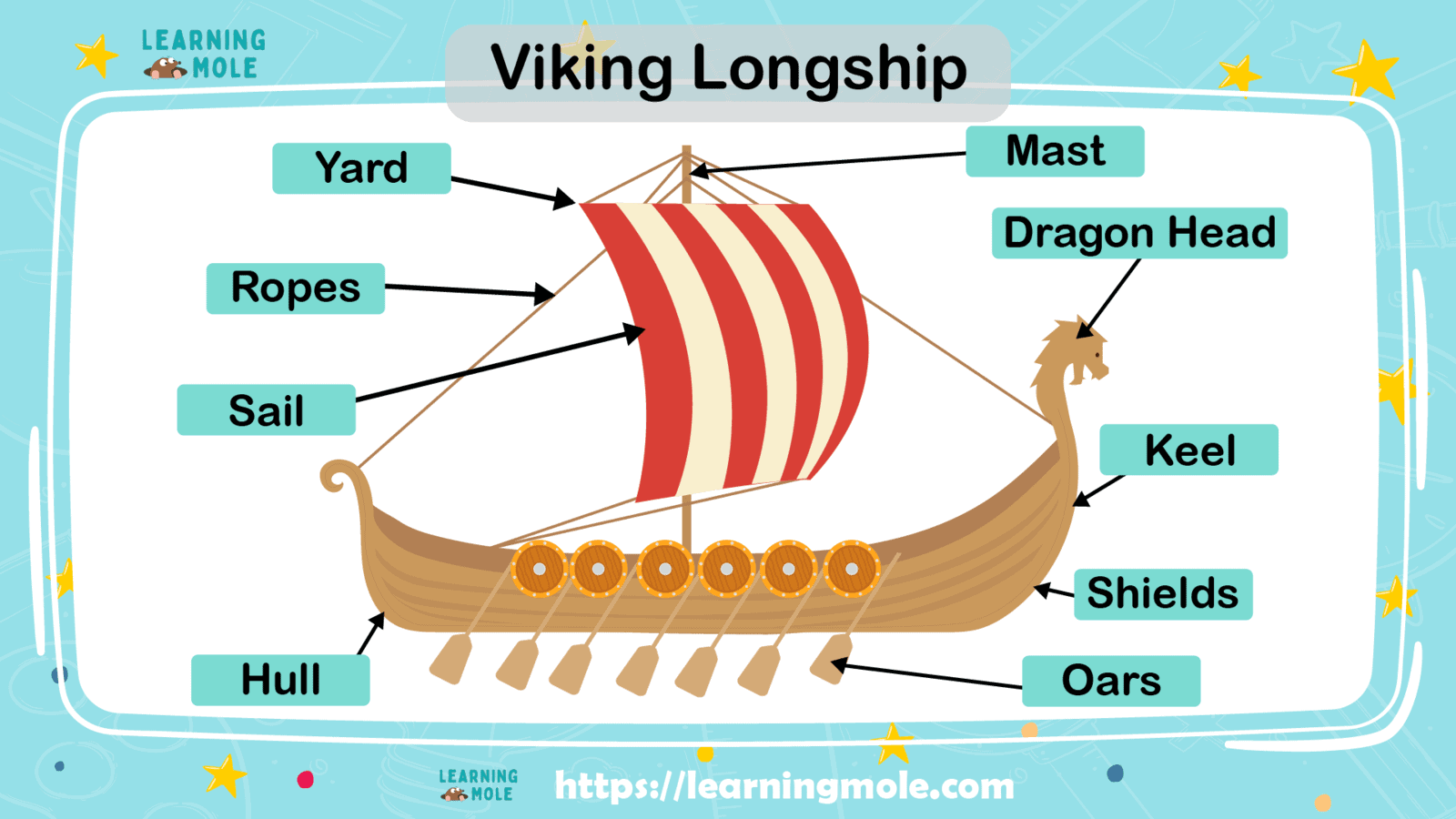
Important information that we must know about the heart of the Viking culture lies the Viking ship. These extraordinary vessels — longships in particular — shaped the lives of the sea-faring Norse and changed the course of European history.
Honed for more than 10 centuries, the shipbuilding skills of the Norse led to a variety of vessels — from small fishing boats and big-bellied cargo vessels to the famous lightning-fast longships used for raiding.
But no matter the size, most of the ships were designed to be narrow with short drafts (vertical distance between waterline and bottom of the ship), features that gave them high adaptability for use in the ocean and rivers.
The Vikings’ ship-building craft reached a high point in the 7th century when they invented the keel, a structural beam that runs from the bow to the stern and sits lower than the main body of the ship.
The Vikings set up colonies on the west coast of Greenland during the 10th century. The Viking sagas tell of journeys they undertook from these Greenland colonies to the New World. They mention places named “Helluland” (widely believed to be Baffin Island), “Markland” (widely believed to be Labrador) and “Vinland” (a more mysterious location which some archaeologists believe could be Newfoundland).
At present the only confirmed Viking site in the New World is located at L’Anse aux Meadows on the northern tip of Newfoundland. That site was excavated in the 1960s. Additionally, there are three possible Viking sites that archaeologists have recently excavated in Canada. Two of the possible sites are located in Newfoundland while a third site is located on Baffin Island in the Canadian Arctic.
10 Vikings Facts & Myths
- The Vikings were seafaring people from the late eighth to early 11th century who established a name for themselves as traders, explorers, and warriors.
- They discovered the Americas long before Columbus and could be found as far east as the distant reaches of Russia.
- The Vikings used vegetable dyes and plants to colour their clothing. By boiling their clothing in these plants the colour would transfer onto them and dye them.
- Some pieces of jewellery that the Vikings wore had symbolic value, such as Thor’s hammers. The god Thor was worshipped by the Vikings.
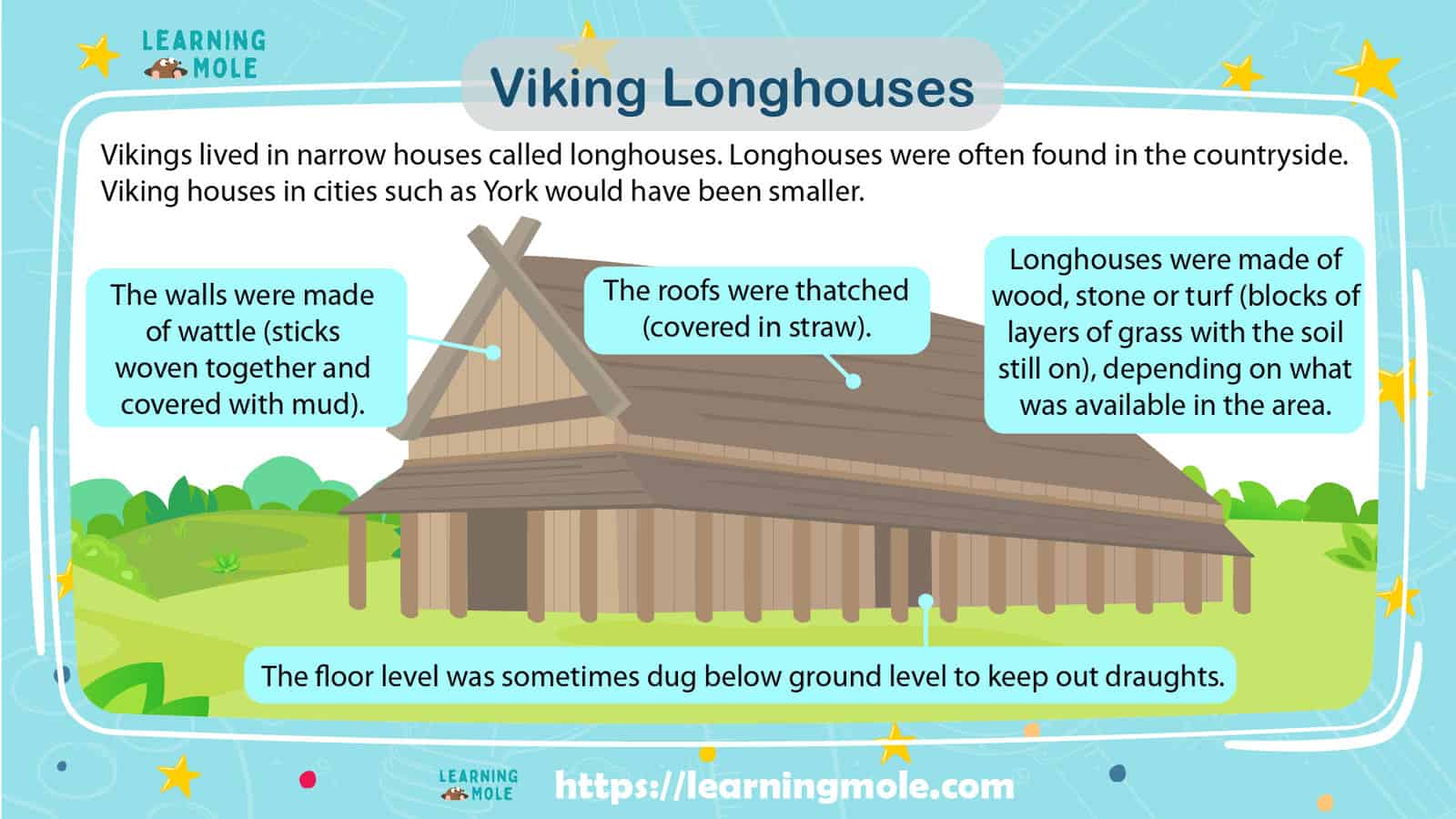
- A longhouse had enough space for 30 to 50 people to live in. This could be one big family with various generations or many smaller sized families all living under the one roof.
- Vikings and their animals all lived together. Storing the animals inside the longhouse with the families meant that the animals stayed dry and warm during wet and cold conditions.
- The majority of longhouses had no windows, and all light came from smoke holes and doors. This meant that the longhouse could be very dull and dark. Stone lamps using fish liver oil, whale oil or seal oil were sometimes used in longhouses for extra light.
- The beds and benches in longhouses were lined with animal skin and straw for warmth and comfort and the pillows were usually stuffed with feathers from birds.
- The Vikings were actually very clean people, and they took pride in their own appearance and the tidiness of their homes. The Vikings were quite ahead of their time as they used tweezers, razors, combs and ear cleaners and they also would’ve bathed at least once a week.
- When a child was born, they were only given one name as the Vikings didn’t have last names. Instead, Viking children would have been named after their father’s name. For example, a Viking boy called Lief would have been known as Lief, son of Toke or Lief Toke-son. Viking children could have also been named after their birthplace or their name could have reflected their personality or appearance.


Leave a Reply