
Amazing 10 Vikings Long Ship Facts
Are you searching for an interesting story with fascinating facts about the Viking long ships for your kids? Animation would be the answer and storytelling is also a huge part of the story, which is the way Learning Mole has done it through this video.
The Viking ships were given two different names, they were either the “long ships” or the “dragon ships”, and the Vikings also had slower passenger and cargo ships which were known as “Knorr’s”. The Vikings were also good at making the small ships which they used for fishing or for the short trips they used to go on.
They came from all around Scandinavia (where Norway, Sweden, and Denmark are today). They sent armies to Britain about the year 700 AD to take over some lands, and they lived here until around 1050.
Table of Contents
How Did the Vikings Travel?
The Norse were excellent and talented shipbuilders. The Norse are exceptionally well known for their longboats. These boats could measure up to 37 meters in length. The boats were relatively narrow so that they could sail on the sea or up rivers. This design helped them raid villages by moving up and down waterways.
The Norse have usually depicted rowing boats, and they did rowboats. They built two different kinds of small boats that either had four oars or six oars that men rowed. However, they also could build larger boats that had up to 50 oars that were used to move the ship.
To move on land, the Norse mostly used horses and carts. In the winter, they sometimes used a sled. They also did a lot of walking in the summer
Vikings: The term simply referred to all Scandinavians who took part in overseas expeditions. During the Viking Age, the land that now makes up Denmark, Norway, and Sweden was a patchwork of chieftain-led tribes that often fought against each other.
Vikings Long ship Facts
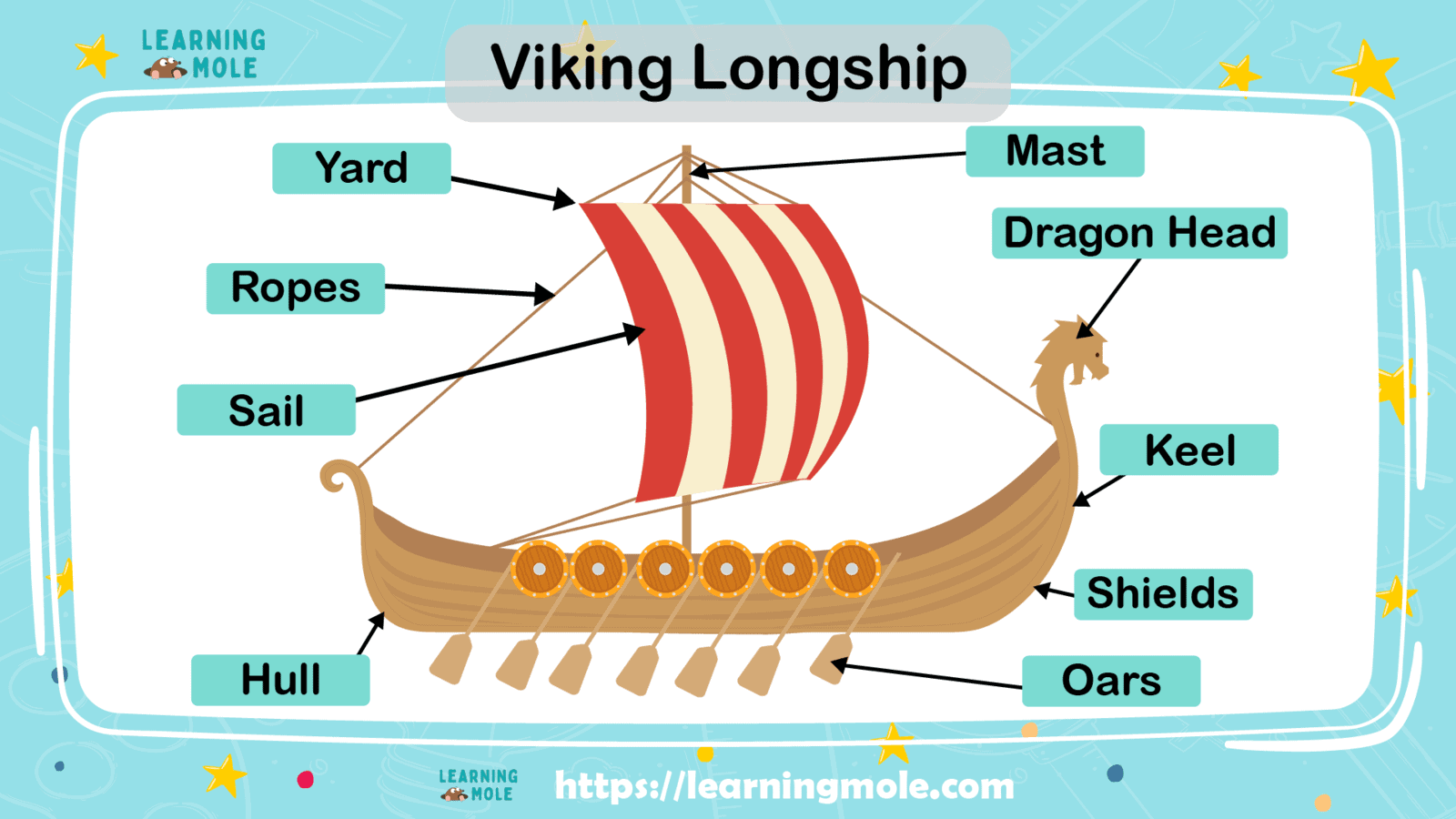
The Vikings are best remembered as fearsome warriors, but their longlisting legacy owes just as much to their seafaring aptitude. Both the Vikings’ ships and the skill with which they utilized them were key to the success of many of their exploits, from fishing and exploring the oceans to raiding.
Though Viking boats came in many shapes and sizes, the most iconic and effective Viking vessel was undoubtedly the long ship. Long, narrow and flat, long ships were fast, durable and capable of navigating both choppy seas and shallow rivers. They were also light enough to be carried over land.
Here are 10 things you may not have known about the impressive long ships.
- Their design evolved over many years
The design principles that led to the Viking long ship can be traced back to the beginning of the Stone Age and the Umiak, a large open skin boat used by people as long as 2,500 years ago. - Viking ships were clinker built
The so-called “clinker” method of ship construction is based on planks of timber, usually oak, being overlapped and nailed together. Spaces between planks were then filled with tarred wool and animal hair, ensuring a watertight ship. - Long ships were able to navigate in shallow waters
A shallow draft allowed navigation in waters as shallow as one meter and made beach landings possible.
- Their top speed was around 17 knots
Speed was variable from ship to ship but it’s thought that the quickest long ships could achieve speeds of up to 17 knots in favorable conditions.
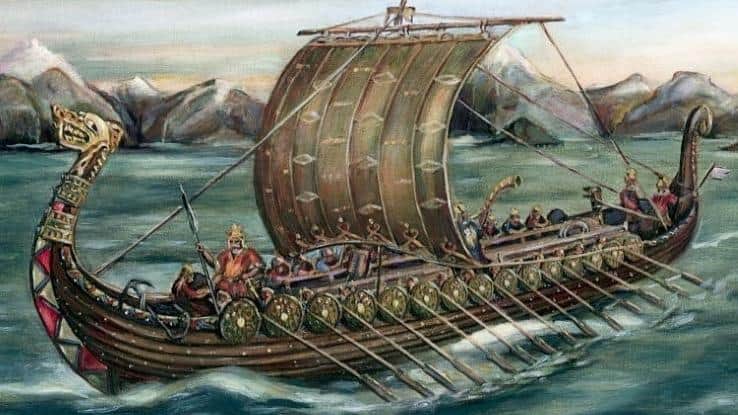

- The boats were typically embellished with decorative headpieces
Skillfully carved animal heads are often featured as figureheads at the front of long ships. These heads – those of dragons and snakes were popular – were designed to provoke fear in the spirits of whichever land the Vikings were raiding. - Longships combined rowing power with wind propulsion
Typically equipped with rowing positions along their entire length, longships also utilized one big square sail, woven from wool. Steering came courtesy of a single steering oar at the back of the ship. - They were double-ended
Their symmetrical bow and stern design allowed longships to swiftly reverse without having to turn around. This was particularly handy when navigating icy conditions.

- Longship classifications were linked to rowing capacity
The Karvi had 13 rowing benches while the Buses had up to 34 rowing positions.
- The vessels were instrumental in enabling the Vikings to explore the globe The breadth of the Vikings’ explorations was remarkable. From North America in the west to Central Asia in the east, the Viking Age is defined by geographically expansive exploration that wouldn’t have been possible without such advanced shipbuilding.
- The longship design was hugely influential
The Vikings’ shipbuilding skills accompanied their extensive travels. Many of the long ship’s characteristics were adopted by other cultures and continued to influence shipbuilding for centuries.
What did the Vikings wear to battle?
Imagine you’re a brave Viking, getting ready for an exciting adventure. You’re going to need some special gear to stay safe and strong in battle. Vikings had cool armor and helmets that helped protect them during their daring journeys.
Viking armor was like a strong, protective suit. It was made of metal, like iron or chainmail, and it covered their bodies to shield them from harm.
The Vikings wore armor on their chests, arms, and legs. It was heavy, but it kept them safe when they fought with their swords and axes. Some Vikings even had shields, which were like big, strong boards made of wood and metal. These shields protected them from enemy attacks.
When you think of Viking helmets, you might picture helmets with big, pointy horns. But here’s a surprise – Viking helmets didn’t actually have horns! They were more like cool, round hats made of metal.
What Was the Norse Religion?
Most of Scandinavia was considered pagan at the time, which means the Vikings came from pagan regions. Slowly, over time, they adopted the Christian religion. Sometimes they blended their religion with the Christians they encountered while raiding British and French villages.
While historians know very little about how the pagans worshipped, they know that many pagan groups had priests or priestesses. Historians also believe that Vikings may have sacrificed horses to the gods.
Like Christianity, their religion believed in diving powers and powerful, supernatural beings. Their ideas about the world stem from the mythologies and stories that are passed down. In these stories, the gods raised the land out of the sea and created Midgard, which is where humans live.
The king of the gods was Odin, who had one eye and was super wise. Then there was Thor, the mighty god of thunder, who carried a big hammer. Freyja was the goddess of love and beauty, and she had a special necklace.
The Vikings believed in these gods and goddesses, and they thought they could help them in their everyday lives.
They also believed in something called Valhalla, which was like a big warrior heaven. When brave Vikings died in battle, they thought they’d go to Valhalla to feast and fight forever. It was a pretty exciting idea for them!
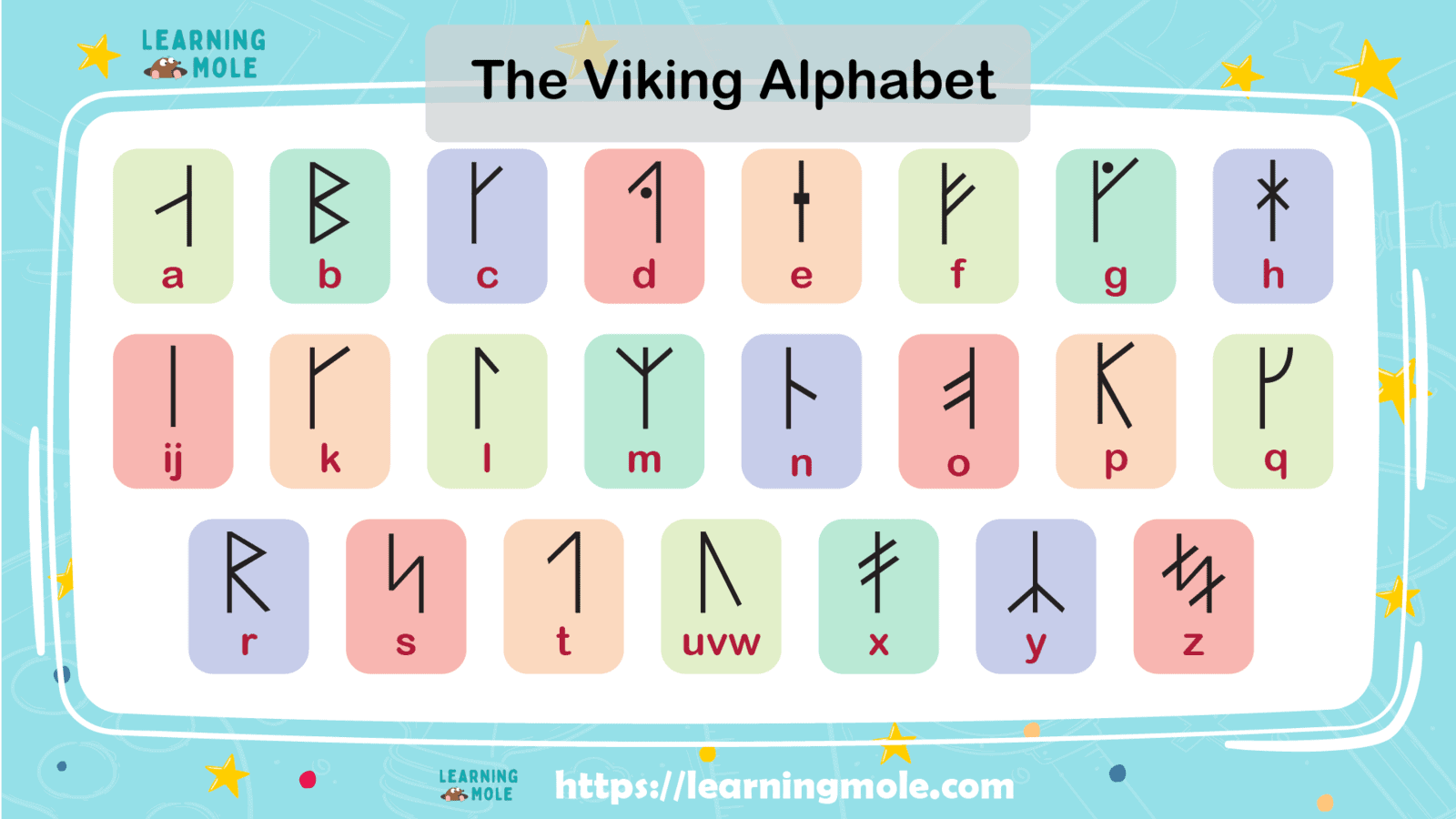
The Vikings even had their own cool runes, which were special letters they used to write their stories and magic spells.
Where Did They Settle?
They settled in many regions. They first moved from Scandinavia to the British Isles, where they raided British villages. They made settlements in Ireland, Scotland, and England, some parts of Wales, and the Isle of Man.
Some of them settled in places like Iceland, which was a land of ice and fire, with volcanoes and hot springs. They built homes, farms, and even held gatherings called “Althings” to make decisions together.
Others traveled west and settled in a place called Greenland, even though it was pretty icy. It was a real challenge to live there, but stubborn as they were they made it work!
Some Vikings ventured even farther and arrived in a land they called “Vinland,” which is believed to be part of North America. They built small settlements and explored the wild forests and rivers.
Some of the Vikings moved to France and started to raid villages in the northern parts of the Frankish Empire. After a peace treaty with the Frankish Empire, the Vikings settled in Normandy.
The Vikings raided and settled across most of the northern hemisphere. So, the Vikings were like bold pioneers, settling in lands near and far, and their adventures shaped the history of these places, leaving behind stories of their brave journeys and discoveries.
What Happened to the Vikings?
The age of the Vikings ended with the Norman invasion in 1066. However, the power of the Norse dwindled towards the end of the 10th century for several reasons. As time passed, the Norse were integrated into European societies and cultures.
Some Vikings became farmers, fishermen, and even traders. They loved telling stories and had cool myths about gods and giants. But after a while, their adventurous days calmed down, and they settled in new lands, like Iceland and even parts of England and France.
Some became kings and queens, and their descendants still live in these places today. The Vikings left a big mark in history, and we can learn a lot about them from their amazing sagas, and the stories they passed down through generations. So, that’s what happened to the brave Vikings – they became a part of history and helped shape the world we know today.



Leave a Reply