
Obesity for Kids: What it Means and How to Prevent it
Do you love burgers and pizza? Does the crunch of chicken pane begin to form saliva in your mouth? Of course, these meals are our favourites, but have you ever thought whether they have nutritional benefits? Unfortunately, all fast foods are unhealthy. In addition, they are among the major risk factors that may cause obesity.
Your weight is essential to your health from the moment you are born. As you get older, you gain weight, and this means that you are growing bigger and getting stronger. An ideal weight depends on age, height and gender (whether you are a girl or a boy). Weighing too much or too little can be a health problem. This article will focus on obesity (excess weight), its meaning and how to prevent it.
Is Obesity A Disease?
Obesity is a complex disease that means gaining a lot of weight.
Obesity Meaning
Scientifically speaking, obesity is an excessive or abnormal accumulation of body fat. This serious medical condition may develop other diseases and health problems that we will discuss later in this article.
What is BMI?
Being obese is not just a number on the scale. To decide if you are obese or not, doctors use BMI, which stands for Body Mass Index. BMI is a weight-for-height screening tool that estimates how much body fat you have. It is your weight in kilograms divided by the square of your height in meters (kg/m2).
How is Obesity Measured?
After a doctor calculates your BMI based on your weight and height, they put the calculation result on a chart to measure obesity. The boys’ chart differs from that of the girls. Doctors use the following categories to describe your weight and decide whether you suffer from obesity:
- Underweight: If your BMI is less than 18.5 kg/m2, you weigh less than the healthy range for your age, height and gender.
- Healthy or Normal Weight: When your BMI is 18.5 to 24.9 kg/m2, you have a perfect weight for your age, height and gender.
- Overweight: If your BMI is 25.0 to 29.9 kg/m2, you weigh more than the recommended weight for your age, height and gender. However, it does not mean that you are obese.
- Obese: When your BMI equals to or is greater than 30 kg/m2, you have higher levels of overweight and weigh much more than what is considered healthy for your age, height and gender.
Obesity Types
Depending on its severity, healthcare providers classify obesity into three different types using BMI.
- Class I Obesity (low-risk obesity) occurs when your BMI is 30.0 to 34.9 kg/m2.
- Class II Obesity (moderate-risk obesity) occurs when your BMI is 35.0 to 39.9 kg/m2.
- Class III Obesity (high-risk obesity) occurs when your BMI is equal to or greater than 40 kg/m2. It is sometimes categorised as “Severe” obesity.
You should check your BMI at least once a year to help doctors determine your overall health risks and their appropriate treatments. However, you should take into consideration that the BMI is sometimes inaccurate because it does not differentiate between fat and muscle. Suppose you are a muscular child. Muscles weigh more than fat. Therefore, you might have a high BMI, although you do not have too much fat in your body.
Obesity Diagnosis
For accuracy, your doctor may perform some recommended tests and physical exams, besides calculating your BMI. They include:
- A General Physical Exam includes:
- Checking vital signs, such as temperature and blood pressure
- Examining your abdomen
- Listening to your heart and lungs
- Your Health History: Your doctor reviews your:
- Eating patterns
- Exercise habits
- Activity levels
- Weight history
- Medical problems
- Medications
- Your Psychological History: Besides reviewing your stress levels, your doctor here checks whether there are any previous incidents of:
- Depression
- Sadness
- Loneliness
- Sleep disturbances.
- Other Health Problems: Your doctor also checks for other possible health problems, like:
- Liver problems
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Your Family’s Health History: Your doctor may check your family’s history of obesity and its related health problems, like diabetes. It is to see if you are at risk for obesity or other medical conditions.
- Blood Tests include:
- Cholesterol test
- Blood sugar test
- Your doctor may also request other blood tests to check for hormonal imbalance.
Some of these blood tests require you to fast. So, ask your doctor if you should not eat or drink before the test and for how long.
Obesity Causes
We all have fat in our bodies, but it turns into an abnormal amount of body fat due to several influences. They may include genetic, behavioural, metabolic and hormonal factors.
1. Food Intake is More Than Energy Consumption
The fundamental cause of obesity is the imbalance between burned and stored calories inside a body, and here is how it goes.
When you eat or drink, you get calories. Your body burns some of these calories to keep your heart beating, lungs breathing, and brain working. It also burns some other calories through daily physical activities and exercises.
Calories you do not burn are stored in your body as fat. The more extra calories you get, the more fat your body will store. Too much fat causes obesity and increases the risk of weight-related health problems.
2. Unhealthy Diets
Obesity may also result from a combination of other factors. Evidence points to an unhealthy diet as the real culprit in obesity for many obese people. You can put in weight if you eat foods high in calories and fats regularly and/or in oversized portions. Sugary drinks also contribute to weight gain. These foods and beverages include:
- Unhealthy vending machine snacks, like chips
- Fast foods and take-out foods
- Ready-made foods
- Baked Goods, like desserts
- Sweets and candy
- Sugary drinks, like soft drinks, sports drinks and fruit juices
3. Less Time Moving Around
As we mentioned before, less physical activity will not burn calories, resulting in abnormal accumulation of body fat. So, you will most likely gain weight if you do not exercise regularly. Additionally, spending a lot of time sitting in front of screens increases your risk of getting obese. Such sedentary activities are numerous, including but not limited to the following:
- Watching TV for several hours
- Playing video games for a lot of time
- Spending too much time looking at tablets, computers and phones
4. Psychological Factors
Another significant factor that may contribute to obesity is feeling that you are under too much pressure. Struggling with stress makes you feel unable to cope with the surrounding circumstances. It may lead you to emotional eating, which means you eat more high-calorie foods to cope with your problems or fight boredom.
5. Genetic and Biological Problems
Additionally, the genetics of your body can increase your risk of obesity. It plays a significant role in how efficiently your body:
- Burns calories
- Converts food into energy
- Regulates your appetite
If you come from a family of obese members, you might be more likely to gain weight. That is because the genes you inherited from your family may affect the amount of fat your body stores and the way your body distributes these fats.
6. Family Inheritance
Obesity may also run in families due to the share of similar eating and activity habits. You can easily put in weight if your family eat high-calorie foods and have a sedentary lifestyle.
7. Social and Economic Issues
In addition, the more time you spend with relatives or friends with obesity, the more likely you will gain weight. This is because you will have access to plenty of unhealthy foods and drinks much of the time. Moreover, you may not know how to cook healthily.
Moreover, you might put in weight if you are in a neighbourhood with lower income. The area you live in might not have safe places to walk or exercise. Further, your region might have limited resources for healthy foods because of their high costs.
8. Certain Diseases and Medications
Obesity can also be traced to certain diseases, like arthritis, Cushing Syndrome and Prader-Willi Syndrome. Arthritis (inflammation or swelling of one or more joints) can lead to decreased physical activity or physical inactivity. Accordingly, it may result in weight gain.
Some drugs can also cause obesity if you do not adopt a healthy lifestyle. These medications include some steroids, antidepressants, diabetes medications and antipsychotic medications.
9. Sleeping Disturbances
Lack of sleep is also another significant factor that can increase your appetite. Similarly, getting too much sleep can contribute to weight gain. Sleeping disturbances can affect the hormones that control your appetite, causing hunger. Consequently, you might eat high-calorie and carbohydrate foods that are the leading cause of obesity.
10. Pictures of Foods and Desserts
Studies show that clothes with printed desserts and candies can increase obesity in children. Suppose you wear a t-shirt with a printed cupcake or doughnut. Whenever you look at the t-shirt, you crave these unhealthy foods. Watching gastronomy or cooking programmes and looking at photos of mouthwatering food can also increase your appetite. Accordingly, you will eat high-calorie and sugary diets and gain extra weight.
Obesity Problems
Obesity prevents you from achieving your dreams and keeping up with your friends on the playground. It also increases the risk of several serious health problems. The following lines list some of the most popular obesity effects on your physical, social and emotional well-being.
1. Type 2 Diabetes
When you eat, carbohydrates break down into glucose. Glucose enters your bloodstream and raises your blood glucose (sugar) levels. In order to control your blood sugar levels, your pancreas produces insulin. Insulin allows the blood sugar to get into the cells throughout your body to provide them with the energy they need.
If you are obese, your cells are unable to respond normally to insulin. Consequently, blood sugar cannot get into the cells, and the cells are unable to get the energy they need to function properly. This condition is called insulin resistance, which may raise your blood sugar levels.
Meanwhile, your pancreas works hard to produce more insulin. It tries to get your cells to respond to insulin again. Extra insulin in your body raises the levels of blood sugar in your bloodstream over time, causing diabetes.
2. High Cholesterol
If you are obese, you have higher levels of free fatty acids, meaning you have more fat tissue in your body. Therefore, it may raise the risk chances of high triglycerides and lead to high cholesterol levels in your blood.
3. High Blood Pressure
Too much fat tissue in your body can also develop obesity-induced hypertension. In fact, fat tissue releases the leptin hormone into your bloodstream. This hormone sends signals to a part of your brain, called your hypothalamus. High levels of leptin indicate that your body reserves sufficient energy. It also triggers the growth of blood vessels in this part, resulting in hypertension.
4. Heart Diseases
Both hypertension and high cholesterol levels contribute to the build-up of plaque in the arteries. As a result, your arteries narrow and harden, thus increasing your risk of heart attack, stroke or other heart diseases.
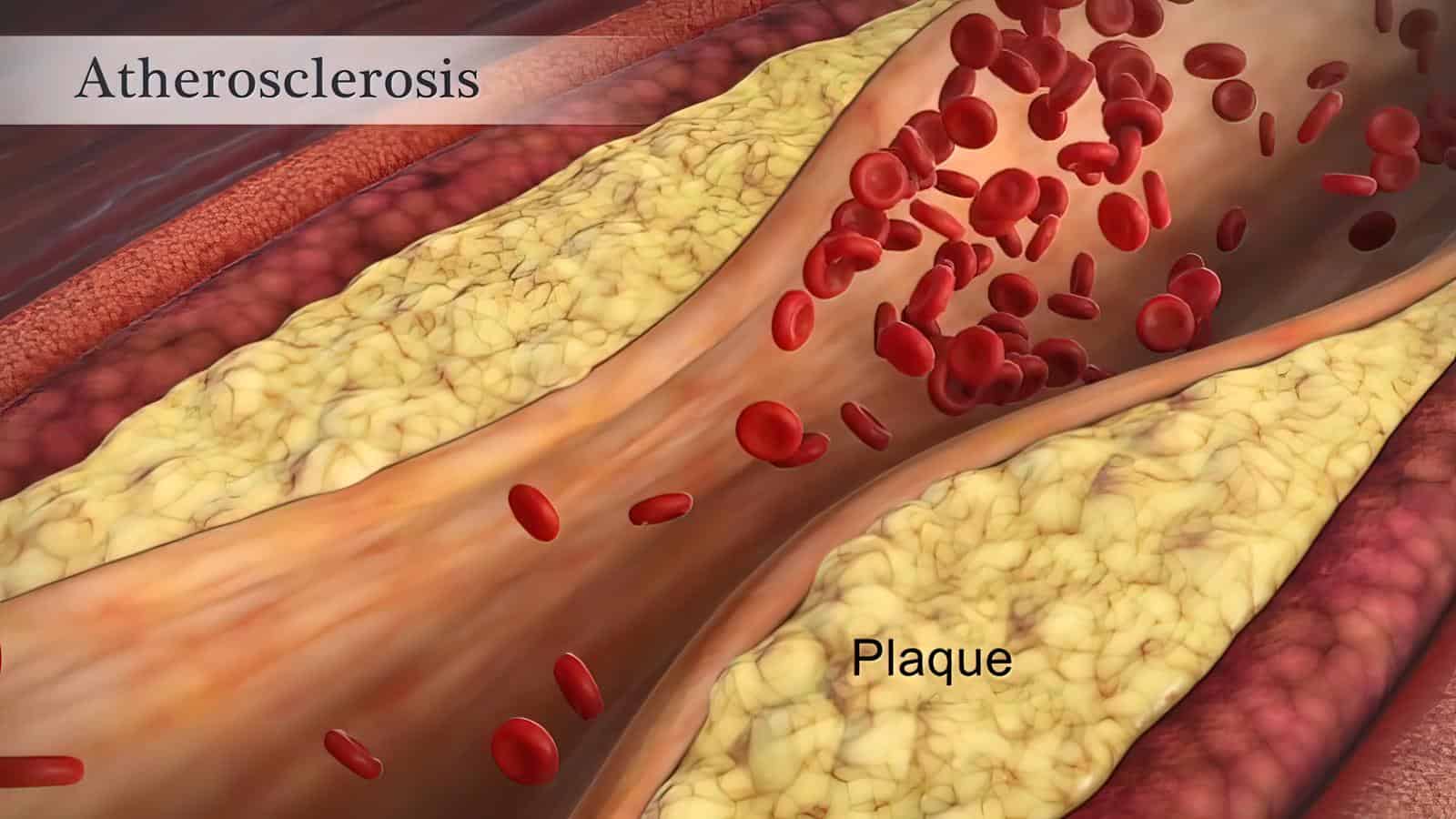
5. Certain Cancers
An obese person may also be more likely to get certain cancers. Their body undergoes changes in genes and levels of insulin and hormones, resulting in cancer in the kidney, colon, rectum, pancreas, liver or gallbladder.
6. Joint Pain
Obesity also causes extra stress on your weight-bearing joints, like your hips and knees, causing pain and injuries in your back, knees and hips. As a result, it may develop a degenerative joint disease called osteoarthritis.
7. Digestive Diseases
Excess weight may also increase the risk of gastrointestinal or digestive diseases, such as Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), heartburn and gallbladder disease. It increases pressure in the abdomen, thus increasing stomach acid leakage. Then, you must likely develop heartburn. In addition, fat builds up in the liver, causing NAFLD, which may lead to liver damage.
8. Breathing Problems
Extra fat on your neck, chest or across your abdomen can also affect your breathing. You will find it hard to breathe deeply. Additionally, it may affect the way your brain controls your breathing. That is why it may most likely develop asthma, obstructive sleep apnea in which breathing frequently stops and starts during sleep, and other respiratory diseases.
9. Social and Emotional Problems
We have mentioned the major health risks caused by obesity. Now, let’s move to the social and emotional problems obesity may cause. The most significant factors that you may experience if you are obese are:
- Discrimination
- Bullying
- Teasing
Additionally, obesity prevents you from enjoying your usual physical activites. Furthermore, you will avoid going to public places because you feel embarrassed. As a result, you may experience:
- Depression
- Anxiety
- Loss of self-esteem
Other weight-related problems that may affect your quality of life are:
- Social isolation
- Shame and guilt
- Disability
- Lower achievement
How to Prevent Obesity
To prevent obesity, focus on your health and apply a healthy lifestyle. Preventing obesity depends mainly on the food you eat, the quantity and the level of exercise.

1. Be Active
The primary factor that will help you avoid extra weight gain is to be active and reduce screen time. Set a time for playing video games or watching TV and stay within the time limit. Recreational screen time should be two hours per day at most. Furthermore, do the physical activities you enjoy every day. You can:
- Play in the backyard of your home
- Exercise
- Skip rope
- Tumble
- Dance
- Run
- Walk
- Jog
- Take the stairs instead of the elevator
- Swim
- Ride a bicycle
- Do some gardening activities, such as raking
- Play a sport that interests you the most, like football, hockey, basketball, tennis, volleyball and hiking
2. Eat Healthy Foods
Your eating habit can also help you stay in shape and avoid obesity. No fast food, soda and sugary drinks. Eat small portions of high-calorie, high-fat and high-sugar foods, like:
- Peanut butter
- High-fat cheese
- Rice
- Full-fat milk
- Mayonnaise
Make sure to pick up healthy food and snacks, which may include:
- Fruits
- Vegetables
- Low-fat milk or yoghurt
- Cottage cheese
- Nuts and seeds
- Whole grain cereal
- Air-popped popcorn without butter
3. Get Enough Sleep
Another significant factor that helps you avoid gaining extra weight is getting enough sleep. Sleeping for a long or short time can cause hormonal imbalances that make you eat a lot during the day, causing obesity. Eight hours of sleep is more than enough.
4. Learn How to Manage Stress
Never let stress manage you. Learn how to manage it instead. Stress is a normal human reaction. Everyone in this world may feel stressed when they:
- Have responsibilities that they find overwhelming
- Become angry or frustrated
- Experience discrimination or abuse
Feeling stressed can increase your appetite and urge you to eat more to cope with the challenges. Never do that! Instead, try to relax and enjoy an activity you love.
- Read your favourite book/novel
- Write in your journal
- Soak in a warm bath
- Take slow, deep breaths
5. Talk to Your Parents
For example, they can:
- Take you on a nature hike to enjoy your time
- Buy groceries
- Reduce unhealthy food
- Cook healthy meals
- Make an appointment with the doctor for check-ups once a year

To sum up
Obesity is an excessive amount of body fat that may cause health problems. In addition, BMI stands for Body Mass Index, which depends on your height and weight. You may be diagnosed with obesity if your BMI is 30 kg/m2 or more.
We also know that obesity may be caused by hormonal, metabolic, genetic and behavioural factors. To prevent it and be healthy, we should eat healthy foods, exercise regularly, reduce screen time, sleep enough and control stress.
If you are diagnosed with obesity, do not get panic. Losing weight is not appropriate for kids. Your doctor will focus on reducing your BMI instead. Taking into account the growth in your height, they slow the progress of weight gain, and this causes your BMI to drop over time.
If you know someone who is obese, bullying and teasing are not acceptable. Never make jokes or make fun of them. Do not also blame the obese person or be biased against them. Instead, respect them and treat them the same way you would like to be treated.


Leave a Reply