
10 Astonishing Heart Facts for Kids
Your heart isn’t just a part of the circulatory system that is responsible for beating and pumping blood to your whole body. It is way more than that. Your heart is a complex organ that works relentlessly every single second. In fact, if it rests, your whole life will stop.
In this article, we are going to talk about ten amazing facts about the human heart. And at the end, we are going to give you 6 things to do to keep your heart healthy.
So get ready for these facts, as some of them you may know for the first time.
1. Your Heart Can Beat Outside Your Body
Yes, your heart can beat even if it is completely disconnected from your body. This is because It has an intrinsic ability to contract on its own. It doesn’t need a signal from your brain to start contracting like other muscles. That is because It has its own conductive system. This conductive system is responsible for keeping your heart beating at a regular rhythm throughout your life.
That is why heart transplantation was one of the early successful organ transplantation surgeries.
Did you know that the first successful open-heart surgery was done more than a century ago, in 1893? It was done by a cardiologist named Daniel Hale Williams in the United States of America.
To know more about this amazing gentleman, see this article.
2. Your Heart Can Grow Stronger With Exercise
You may think that your heart can’t grow stronger with exercises like your biceps, triceps or any other skeletal muscle. But this is not true.
Although your heart is made up of a special type of muscle (that is different from skeletal and smooth muscles), every time you exercise, your heart beats faster and gets stronger.
Doing exercise can affect improve your heart in different ways, as follows:
- It lowers your blood pressure. This will make it easier for your heart to push blood to other organs. Low blood pressure means less resistance and, thus, less effort required from your heart to push that blood.
- It decreases the level of stress hormones. These hormones can be harmful if kept high for a prolonged period.
- Exercise also increases the level of good cholesterol in your blood (HDL: high-density lipoprotein). This is a protective factor against developing heart diseases such as angina.
- It helps in weight reduction by burning calories. This means it lowers the risk of developing health problems associated with obesity.
Now we have talked about some benefits of exercise on your heart. But you may be wondering what kind of exercise I should do to keep my heart healthy and strong.
Well, according to the American Heart Association, the best type of exercise for your heart is a combination of aerobic exercise, also known as cardio (like swimming, running, and bicycling), with resistance training (like weightlifting, squats, push-ups, and using resistance bands).
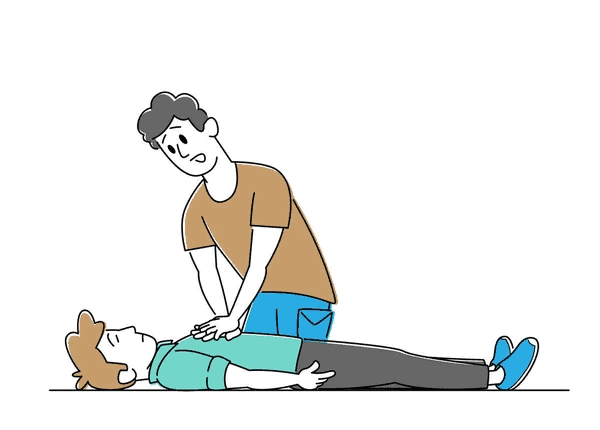
3. Your Heart Can be Revived After Stopping for a Few Seconds.
If your heart stops suddenly, it is called cardiac arrest. It may be fatal if left untreated, as when your heart stops beating, it can’t pump blood to other body organs. This is so dangerous for some vital organs in your body, like your brain, which can’t live long without a blood supply.
That is why you should learn how to do cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR).
CPR is one of the essential first aid techniques any doctor or a non-medical person should know. It involves doing chest compression (to revive your heart) and sometimes mouth-to-mouth breathing (to revive your lungs).
Who knows, you may save someone’s life by learning how to do CPR. It’s better to know how to do it as early as possible. You never know when you are going to need it.
To know more about how to do CPR, check out this article. Or watch this animated video below;
4. Your Heart Rate is 80 Beats per Minute on Average
The number of heartbeats per minute is called the heart rate. The normal heart rate of an adult ranges from sixty to one hundred beats per minute. So, if you do the math, you get an average of 80 beats per minute (60 + 100/ 2).
If you multiply that number by the number of minutes in a day (24 * 60), you will get an average of 115.200 beats every day. What an enormous effort this organ makes every day. Isn’t that wonderful?
You may notice that your heart beats stronger when you see someone you love or when you are going to an important interview or exam.
This is because your heart rate isn’t constant all the time, and it changes according to different factors such as:
- Age
- Sex (men have slower heart rates than women)
- Physical activity
- Smoking
- Emotions
- Medications
If your heart rate is higher than 100 beats per minute, it is called tachycardia (Tachy means fast, and cardia means heart in Greek. So it all translates into “fast heart”).
Things that increase your heart rate may be physiological or pathological. They include:
- Coffee
- Stress
- Adrenaline (a hormone that is released during stress and fear)
- Smoking
- Hyperactive thyroid gland
- Some illegal medications like cocaine
- Anaemia
On the other hand, if your heart rate is slower than 60 beats per minute, it is called bradycardia (Brady means slow, and cardia means heart. So together they mean “slow heart”)
Things that slow down your heart rate include:
- Sleep
- Underactive thyroid gland
- Some medications like sedatives and opioids
Slowing or racing your heart rate is a healthy body response, and you don’t need to worry about it. However, you may need to consult your doctor if the condition is associated with other signs and symptoms.
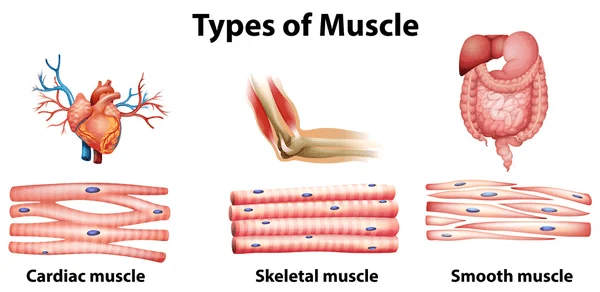
5. Your Heart Muscles are Very Specific
Your heart has a unique type of muscle that is distinctive from the two major muscle types in our body. These are the skeletal and the smooth muscles. To know the difference between those three types, let’s talk about each type separately.
The Skeletal Muscles
Skeletal muscles are those in your biceps, triceps, and quadriceps. They are called skeletal because they are attached to your skeleton (bones). And because they are attached to your skeleton, they are responsible for moving your body parts on your will (voluntary movements).
They help you Walk, stand, jump, dance, hold a book to read, type on your keyboard, and write your homework. All these tasks would be nearly impossible without your skeletal muscles.
If you take a look at these muscle fibres under the microscope, you will find them striated (they have transverse strands).
The Smooth Muscles
On the other hand, smooth muscles are the man behind the camera. You can’t feel them while they work. They work in silence as they are responsible for the involuntary movements of your body.
They are present in your stomach, small intestine, blood vessels, and urinary bladder. All these structures have smooth muscles in their wall to help them move and do their function. But you can’t feel them. For example, you can’t feel your stomach contraction to propel the food down to your small intestine to be digested and absorbed.
These muscles don’t have strands under the microscope, which is why they are called smooth muscles.
The Cardiac Muscles
Now, the unique muscle type that is present in your heart; the cardiac muscle. It has mixed characteristics of both smooth and skeletal muscles.
It is an involuntary muscle (it moves on its own, which is a smooth muscle feature), but it is made up of striated muscles like the skeletal muscles. These unique features led the scientists to put it in a separate category apart from skeletal and smooth muscles.
6. Men’s Hearts are Somehow Different From Women’s Hearts
Although both have the same structure and function, men’s and women’s hearts are a little bit different. For example, women’s hearts beat faster than men’s hearts. Also, men’s hearts are heavier than women’s hearts.
Wait a minute. Don’t get me wrong here; I didn’t say men’s hearts are better than or healthier than women’s hearts. In fact, women have better hearts and fewer heart problems than men.
7. Your Heart Size is Almost the Same as the Size of Your Fist
Our heart sizes vary from person to person. But you can estimate the size of your heart by making a fist with your hand, and your heart size would be nearly the same size as your fist.
Heart size also varies across the different types of animals, with whales having the largest hearts and the fairy fly (a type of wasp) having the smallest heart in the world. It is so small that you need a microscope to see it clearly.
8. It has Four Chambers (two Atria and two Ventricles)
Our heart is composed of four chambers: two atria (the singular word of which is atrium) and two ventricles. They are kept separate by valves. These valves allow blood to move in one direction from one chamber to the other. That way, the blood moves in one direction and can’t go back.
Some animals, however, have different heart structures. For example, a frog has a heart with three chambers (two atria and one ventricle). A fish, on the other hand, has a heart with only two chambers (one ventricle and one atrium)
To know more about how your heart works and your cardiovascular system, check out this article or watch the video below.
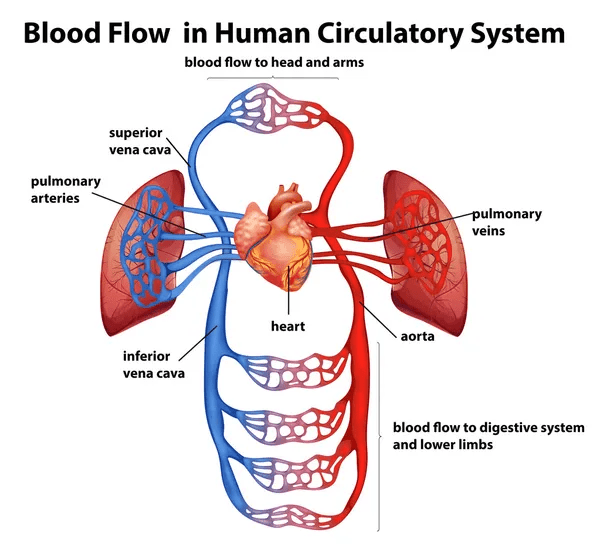
9. The Blood Coming to it is Purple, and out of it is Red
You may have already heard of the circulatory system at school and know how blood moves inside your body. So, let’s go through it one more time.
- First, the deoxygenated blood moves from your whole body to the heart through the superior and inferior vena cava.
- It then enters your heart through the right atrium and then moves to the right ventricle.
- Then, the right ventricle pushes it to the lungs.
- Inside your lungs, the blood gets saturated with oxygen that you breathe from the air.
- The oxygenated blood then moves from your lungs to the left side of your heart (the left atrium, then the left ventricle).
- Finally, the left ventricle pumps this fresh oxygenated blood back to your whole body. And this cycle repeats itself again eighty times every single minute.
10. Heart Cancer is Very Rare
Heart cancer is the least you should worry about among the other various types of cancer. The reason why your heart is very unlikely to get cancer is so simple.
Our heart cells are very limited when it comes to division and regeneration. And that is exactly what cancer is; it is defined as uncontrolled cell division and multiplication. So how can it get cancer if it does not have the ability to divide and multiplicate?
Conclusion
Your heart is a unique and precious organ, and you must keep it healthy. You can do so by keeping a simple and healthy lifestyle.
Here are 6 things to do to keep it healthy and strong:
- Do exercise regularly. Especially aerobic and resistance training exercises.
- Eat healthy food. Exercise alone is not enough to have a healthy body. You need to watch out for what you get into your body. A healthy diet is that which contains less saturated fats and more vegetables and fruits.
- Stay away from smoking and long-term stress.
- Try to reduce your weight.
- Keep your blood pressure and cholesterol level under control.
- And don’t forget to laugh; it is good for your heart, too.
And finally, the heart shape that you draw does not have anything to do with the real shape of our hearts.
Some relevant articles that might interest you:
- Want to know more about your heart and cardiovascular system in detail? Check out this one.
- To know more about your skeletal system, check out this article.
- Want to know more about your urinary system, check out this article.


Leave a Reply